2020-02-25 21:54:07
Carlos Vila, Arturo Tortosa, Gonzalo Blay, M. Carmen Mun˜ozb and Jose´ R. Pedro
Introduction
The catalytic asymmetric Friedel–Crafts reaction1 of aromatic compounds with imines is one of the most important methodologies for the synthesis of enantiopure chiral benzylic amines, which are present in a wide range of pharmaceutical and natural products. In this context, the enantioselective addition of indoles to imines is one of the most studied asymmetric Friedel–Crafts reactions,3,4 due to the importance of the indole scaffold in natural product synthesis, medicinal and agrochemical industries and materials science.5 However, the majority of methods on the enantioselective aza-Friedel– Crafts reaction of indoles involve the functionalization of the C-3 position.4 Additionally, different examples of the asymmetric functionalization at the C-2 position of indoles with imines have been described.6 In contrast, the enantioselective functionaliza- tion in the carbocyclic ring of indoles is hardly studied in the literature and represents a great challenge in asymmetric catalysis (Fig. 1A).7 We have recently presented a methodology for the organocatalytic enantioselective functionalization of the carbocyclic ring of indoles using as an activating/directing group, a hydroxy group.8–10 Hydroxyindoles, in the presence of bifunctional organocatalysts, react as phenols, even when the positions in the azole ring remained unsubstituted. Given the remarkable significance of chiral indoles bearing a nitrogen in the a-position and hydroxyindoles (Fig. 1B), the development of new methodologies for the synthesis of chiral indolyl amines is the great interest for organic synthesis.
In this communication, to accomplish the enantioselective functionalization in the carbocyclic ring of indoles, we have chosen cyclic imines (benzoxathiazine 2,2-dioxides) as electro- philes. Very recently, benzoxathiazine 2,2-dioxides have attracted attention in asymmetric catalysis, because these compounds have been proved to be powerful building blocks for the synthesis of chiral benzosulfamidate heterocycles. In this context, several sulfamidates have shown important biological activities11(Fig. 1C) and several examples of enantioselective reactions have been described using these cyclic imines as electrophiles.12 However, the number of enantioselective aza-Friedel–Crafts reactions using benzoxathiazine 2,2-dioxides is scarce.13,14 In 2017, Kim has described the organocatalytic enantioselective alkylation of indoles at the C-3 position with cyclic imines catalyzed by chiral Brønsted phosphoric acid (Scheme 1A).13a The corresponding 3-indolyl sulfamidate derivatives were obtained with excellent yields and enantioselectivities. Herein, we described a comple- mentary methodology for obtaining chiral indolyl sulfamidates (Scheme 1B). By using a quinine-derived bifunctional organo- catalyst, we achieve the functionalization of the carbocyclic ring of hydroxyindoles with cyclic imines, obtaining 4-indolyl, 5-indolyl and 7-indolyl sulfamidate derivatives.
Results and discussion
We chose the aza-Friedel–Crafts reaction between benzoxathiazine 2,2-dioxides (1a) and 4-hydroxyindole (2) for the optimization studies. Different bifunctional organocatalysts derived from Cinchona alkaloids (Fig. 2) in CH2Cl2 at room temperature were screened (Table 1). When quinine (I) was tried as a catalyst, the regioselectivity was poor and we observed 3 compounds after 21 h of reaction (Table 1, entry 1). The major product was the corresponding hydroxyindole alkylated at the C-5 position (3a) in 48% yield but was a racemic mixture. Then, we isolated as an inseparable mixture after column chromatography, the product alkylated at the C-7 position (4a) and the double alkylated product at C-5 and C-7 positions (5a, a mixture of diastero- isomers in 1 : 1 ratio determined by 1H NMR). Different bifunc- tional organocatalysts such cupreines, thioureas and squaramides were tested,15 but we found that 9-O-benzylcupreine (II), derived from quinine, was the only one with a promising enantio- selectivity (33% ee, entry 2). However, product 5a was still obtained with high quantity (28%). We tried several cupreine derivatives with a variety of substituents on the secondary hydroxyl group. The best catalyst in terms of enantioselectivity was catalyst XI, giving compound 3a in 48% yield, and 43% ee in 6 h (entry 11).
Next, we examined different solvents (Table 2), obtaining the best enantioselectivities with chlorinated solvents. In particular, when the reaction was run in 1,2-dichloroethane, compound 3a was obtained with 57% ee (entry 3, Table 2).
Then, the effect of the reaction temperature was investigated. By lowering the reaction temperature to 4 or —20 1C, or increasing to 501C, the enantioselectivity was worse than that at room temperature. Afterward, different concentrations (entry 13 and 14) were tested without any improvement in the enantiomeric excess. Finally, different catalyst loadings were evaluated (entries 15–17), obtaining an enhancement of the enantiomeric excess to 67% ee and 46% yield, when 2 mol% of catalyst was used (entry 16). Our efforts to improve the enantiomeric excess of compound 3a were unsuccessful; therefore, we decided to study the scope and generality of the reaction under the conditions shown in entry 16, Table 2.
First we studied the effect of the substituents in the cyclic imines using 4-hydroxyindole as a nucleophile (Scheme 2). The presence of a strong electron-donating group (MeO) at the 6 position led to a nearly racemic mixture, while the presence of electron-withdrawing groups at the 6 position (Br) led to an improvement of the yield of product 3d to 89%16 maintaining the enantioselectivity (70% ee). Once that we studied the reaction with 4-hydroxyindole, we decided to apply our methodology for the functionalization of indoles in every position of the carbocyclic ring. So, we continued our research studying the reaction of 5-hydroxyindole (6) and differently substituted benzoxathiazine 2,2-dioxides. To our delight, the corresponding product 7a, regioselectively alkylated at the 4 position, was obtained with good yield (71%)17 and good enantiomeric excess (80% ee). The introduction of substituents in the aromatic ring of the cyclic imines revealed that both electron-donating and -withdrawing groups were well-tolerated at the 6 position on the ring (7b–7d, 89–98% yield and 84–85% ee). Moreover, cyclic imines (1e–1f) with two substituents that provide steric hindrance were suitable substrates for the aza-Friedel–Crafts reaction, affording good enantiomeric excess (86% ee) and good yields (99% and 73%). In addition, benzoxathiazine 2,2-dioxides bearing func- tional groups in the 8-position were also tolerated as substrates giving the reaction product 7g, with good yield (95%) and enantiomeric excess (81%). However, a naphthyl ring was not tolerated and the corresponding product was obtained with a moderate yield and enantioselectivity.18 Unfortunately, 6-hydroxyindole showed low reactivity under the optimized reaction conditions, the 7-alkylated product 9a was obtained with complete regioselectivity, but a moderate yield (51%) and low enantioselectivity (37% ee) after 3 days of reaction. Finally, 7-hydroxyindole was also tested under the optimized reaction conditions, but unfortunately the regioselectivity was low obtain- ing a ratio of 1 : 1 of alkylated products at C-6 and at C-4, and the enantiomeric excesses of these compounds were also very poor.15 We attribute these results to the interference between the NH of the indole group and the hydroxyl group.
The absolute configuration of compounds 3e and 7a was determined to be (R) by X-ray analysis19 (Scheme 2), and for the rest of the products 3 and 7 was assigned on the assumption of a uniform mechanistic pathway. The observed stereochemistry can be explained through a plausible transition state depicted in Scheme 3, where the catalyst activates both the nucleophile and the electrophile through hydrogen bonding. The hydrogen bonding between the quinuclidine tertiary amine and the hydroxyl group of indole can be ascertained due to the different reactivities of 5-methoxyindole (10). When 10 was used as a nucleophile under the optimized reaction conditions, the reac- tion took place at the C-3 position of the indole (the normal position for a Friedel–Crafts alkylation) and the corresponding product 11 was obtained with good yield (73%), but nearly racemic (6% ee).
Finally, we carried out the reduction of the sulfamidate moiety20 of compound 7a (Scheme 4), using LiAlH4 obtaining the corresponding chiral amine bearing phenol and hydroxyindole moieties, which was protected in situ as its Boc derivative 12, with good yield (59%) and preserving the enantiomeric excess of compound 7a (81% ee).
Conclusions
In summary, we have described an enantioselective functionalization in the carbocyclic ring of indoles through an aza-Friedel– Crafts alkylation reaction of hydroxyindoles with benzoxathiazine 2,2-dioxides as electrophiles using a quinine-derived bifunctional organocatalyst. The corresponding chiral sulfamidates were obtained with good yields and from moderate to good enantio- selectivities. In general, the best yields and enantioselectivities were obtained when 5-hydroxyindole was used as a nucleophile, the reaction occurring at the C-4 position of the carbocyclic ring. This methodology represents the first Friedel–Crafts alkylation in the carbocyclic ring of indoles with cyclic imines.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
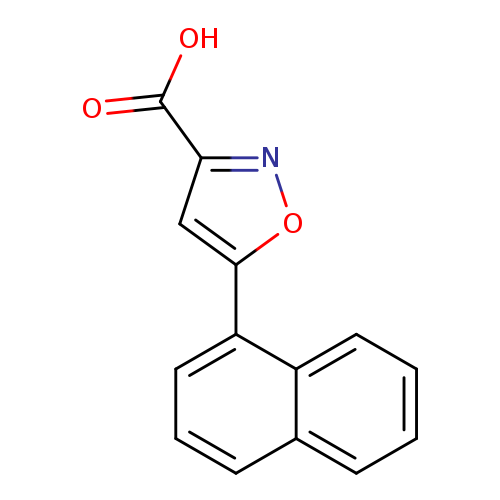
5-(1-Naphthyl)isoxazole-3-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA01AR1E CAS No.:1105193-50-7 MDL No.:MFCD07377191 MF:C14H9NO3 MW:239.2262 |
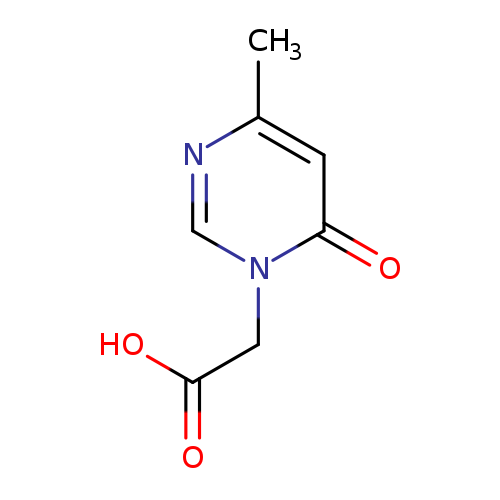
(4-METHYL-6-OXOPYRIMIDIN-1(6(H))-YL)ACETIC ACIDCatalog No.:AA01AQ5S CAS No.:1105193-55-2 MDL No.:MFCD12402755 MF:C7H8N2O3 MW:168.1500 |
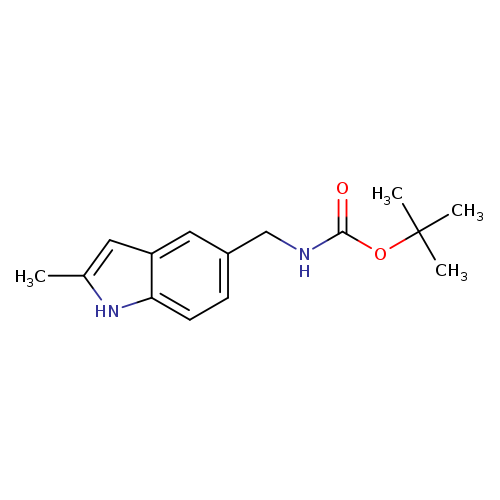
TERT-BUTYL (2-METHYL-1H-INDOL-5-YL)METHYLCARBAMATECatalog No.:AA01AQID CAS No.:1105193-63-2 MDL No.:MFCD16652916 MF:C15H20N2O2 MW:260.3315 |
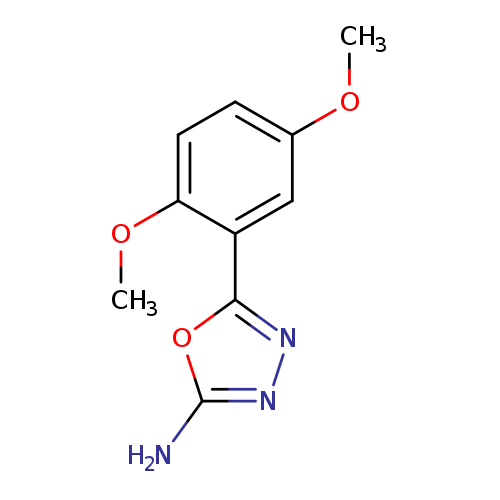
5-(2,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA0191K2 CAS No.:1105193-64-3 MDL No.:MFCD11986944 MF:C10H11N3O3 MW:221.2126 |
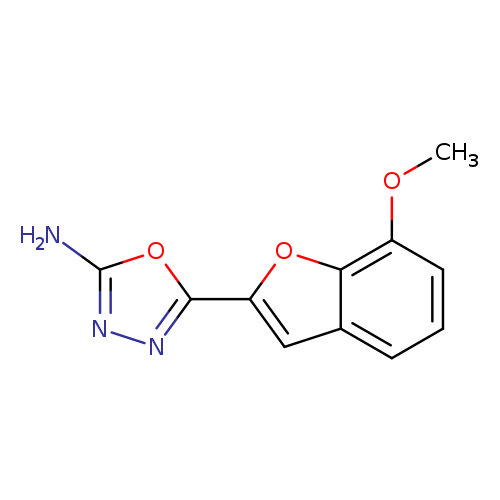
5-(7-Methoxybenzofuran-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA0191K4 CAS No.:1105193-69-8 MDL No.:MFCD11986945 MF:C11H9N3O3 MW:231.2075 |
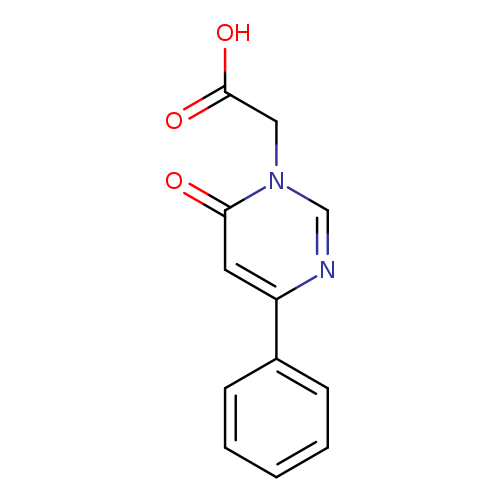
2-(6-oxo-4-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-1-yl)acetic acidCatalog No.:AA01BBXH CAS No.:1105193-70-1 MDL No.:MFCD16652659 MF:C12H10N2O3 MW:230.2194 |
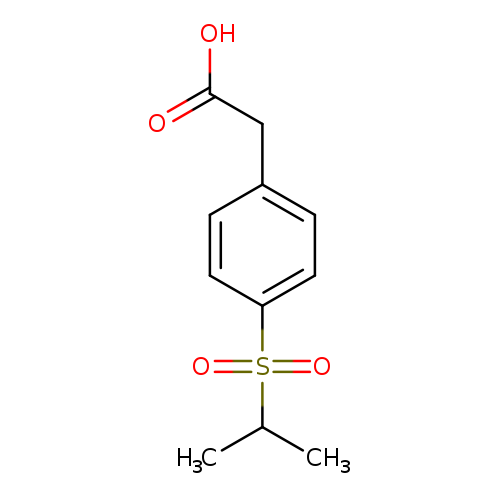
2-[4-(propane-2-sulfonyl)phenyl]acetic acidCatalog No.:AA01AHNU CAS No.:1105193-73-4 MDL No.:MFCD11986718 MF:C11H14O4S MW:242.2915 |
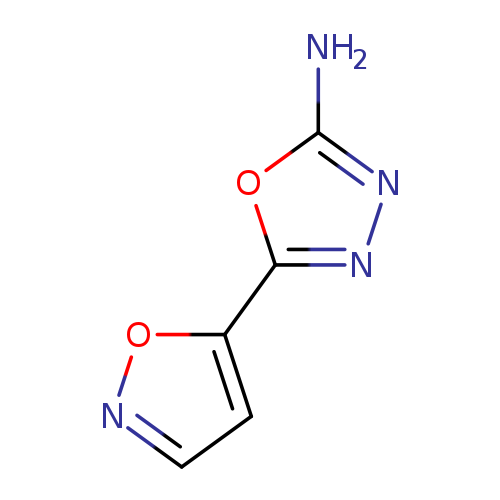
5-Isoxazol-5-yl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA00VRZG CAS No.:1105193-74-5 MDL No.:MFCD11986946 MF:C5H4N4O2 MW:152.1109 |
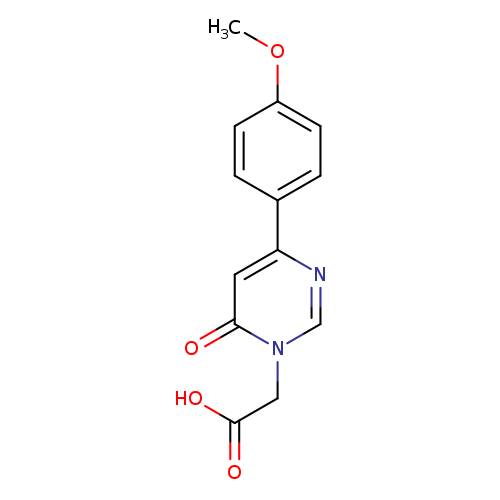
[4-(4-METHOXYPHENYL)-6-OXOPYRIMIDIN-1(6(H))-YL]ACETIC ACIDCatalog No.:AA01AQAF CAS No.:1105193-75-6 MDL No.:MFCD16652660 MF:C13H12N2O4 MW:260.2454 |
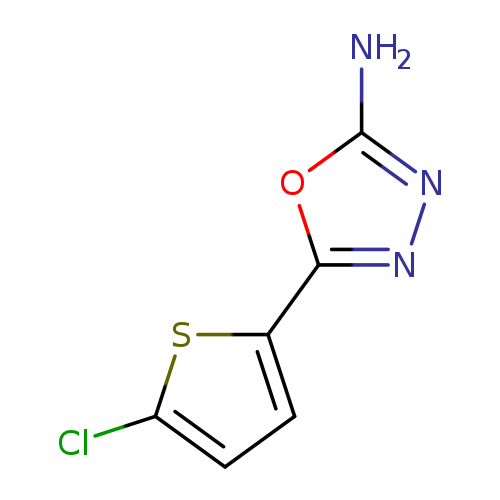
5-(5-Chlorothiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA0092GE CAS No.:1105193-79-0 MDL No.:MFCD11986949 MF:C6H4ClN3OS MW:201.6335 |
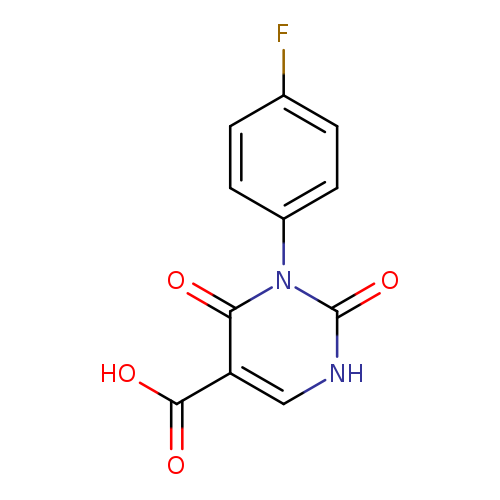
3-(4-FLUOROPHENYL)-2,4-DIOXO-1,2,3,4-TETRAHYDROPYRIMIDINE-5-CARBOXYLIC AC+Catalog No.:AA01AQES CAS No.:1105193-80-3 MDL No.:MFCD16631563 MF:C11H7FN2O4 MW:250.1827 |
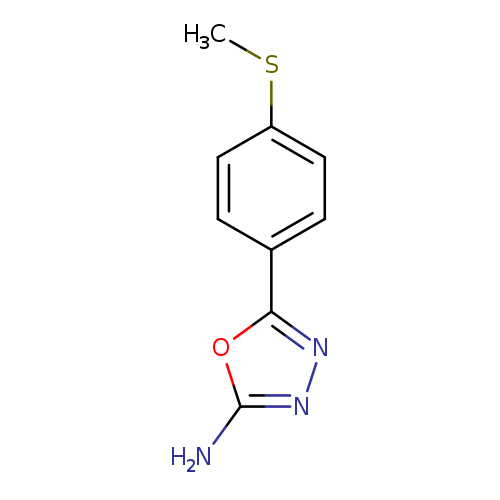
5-[4-(Methylthio)phenyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA0191K7 CAS No.:1105193-84-7 MDL No.:MFCD11986950 MF:C9H9N3OS MW:207.2523 |
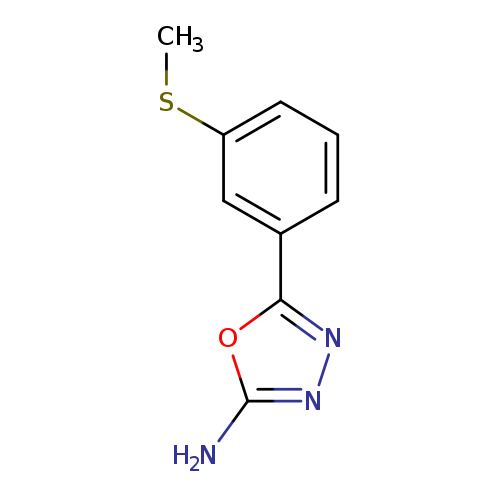
5-(3-(Methylthio)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA0191K8 CAS No.:1105193-89-2 MDL No.:MFCD11986951 MF:C9H9N3OS MW:207.2523 |
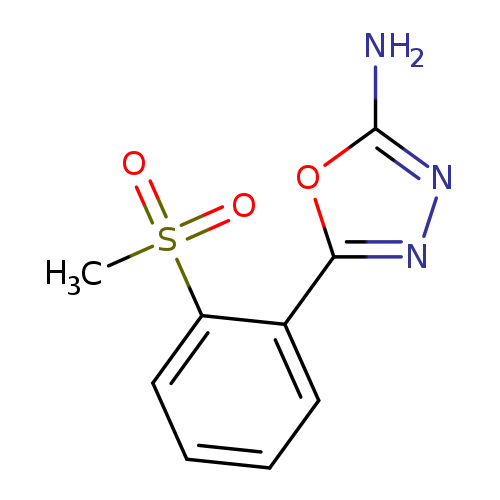
5-[2-(METHYLSULFONYL)PHENYL]-1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-AMINECatalog No.:AA01ARQC CAS No.:1105193-94-9 MDL No.:MFCD11986952 MF:C9H9N3O3S MW:239.2511 |
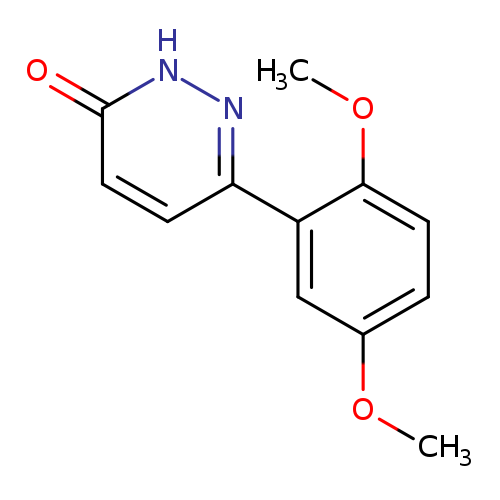
6-(2,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)pyridazin-3(2H)-oneCatalog No.:AA018FPL CAS No.:1105193-95-0 MDL No.:MFCD12531089 MF:C12H12N2O3 MW:232.2353 |
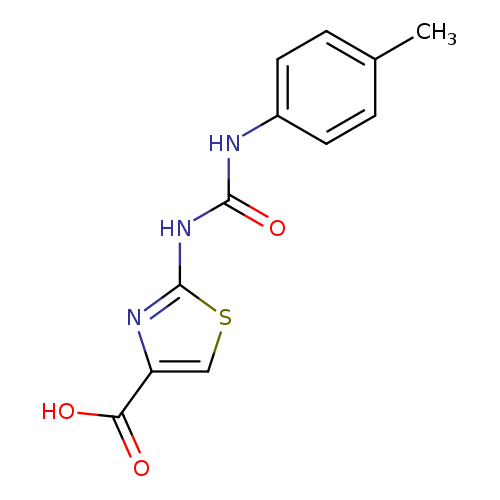
2-(([(4-Methylphenyl)amino]carbonyl)amino)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA01ART7 CAS No.:1105193-98-3 MDL No.:MFCD11986722 MF:C12H11N3O3S MW:277.2990 |
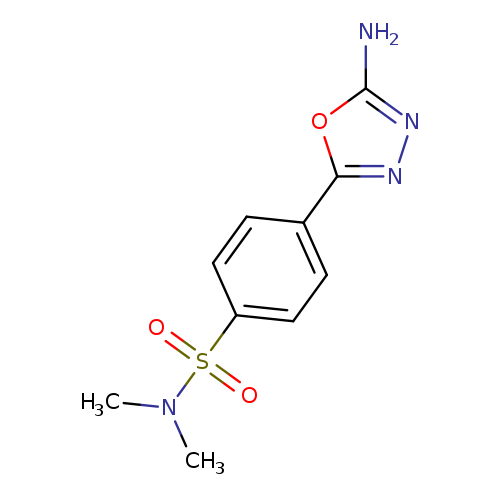
4-(5-Amino-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-n,n-dimethylbenzenesulfonamideCatalog No.:AA01ARQD CAS No.:1105193-99-4 MDL No.:MFCD11986953 MF:C10H12N4O3S MW:268.2923 |
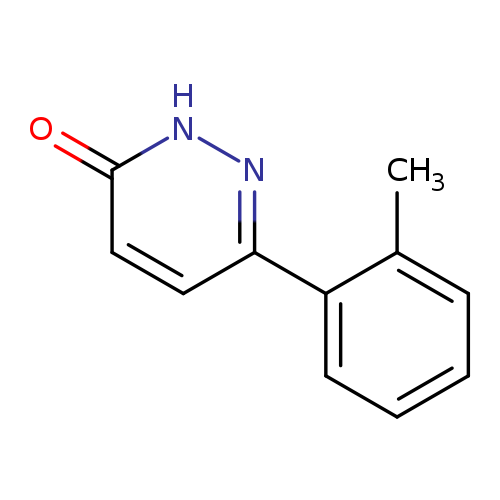
6-(o-tolyl)pyridazin-3(2H)-oneCatalog No.:AA018FPG CAS No.:1105194-00-0 MDL No.:MFCD12143090 MF:C11H10N2O MW:186.2099 |
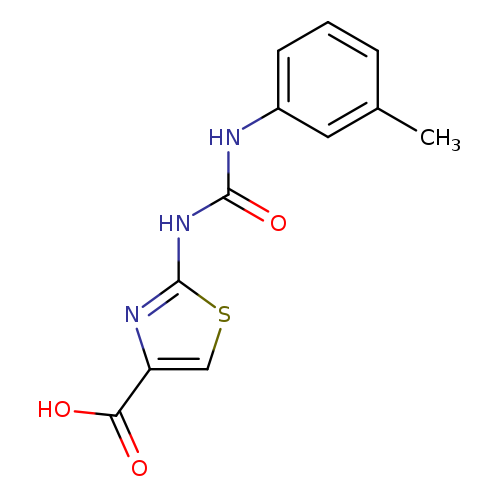
2-(([(3-METHYLPHENYL)AMINO]CARBONYL)AMINO)-1,3-THIAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACIDCatalog No.:AA01ART8 CAS No.:1105194-03-3 MDL No.:MFCD11986723 MF:C12H11N3O3S MW:277.2990 |
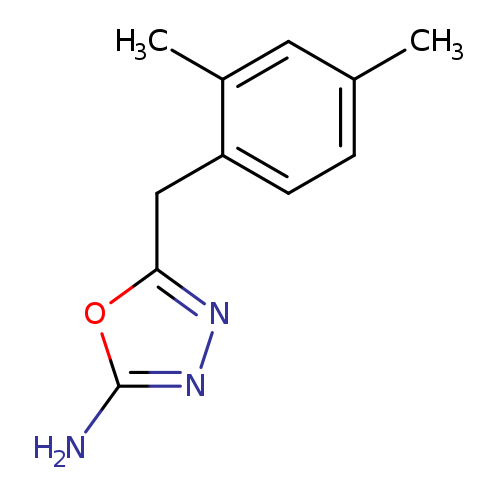
5-(2,4-Dimethylbenzyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA0191KE CAS No.:1105194-04-4 MDL No.:MFCD11986954 MF:C11H13N3O MW:203.2404 |
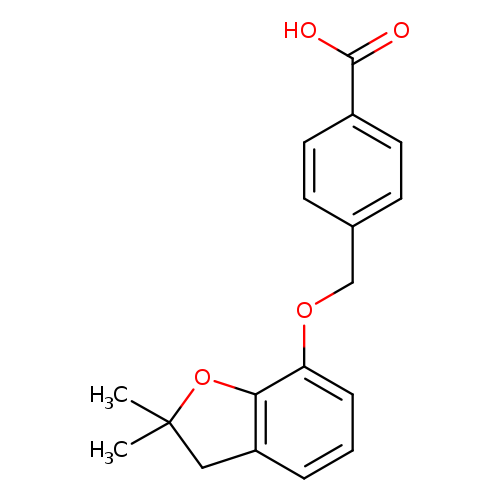
4-([(2,2-Dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-7-yl)oxy]methyl)benzoic acidCatalog No.:AA01ART9 CAS No.:1105194-08-8 MDL No.:MFCD11986724 MF:C18H18O4 MW:298.3331 |
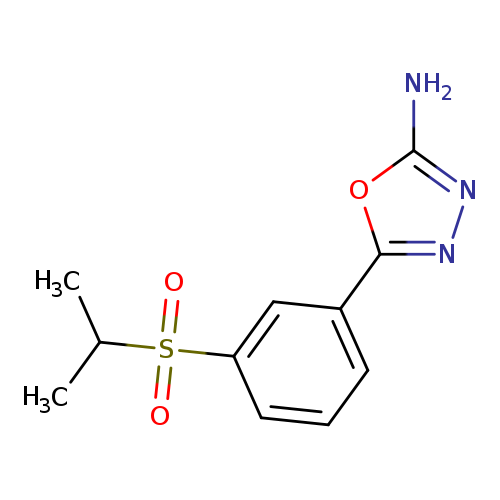
5-[3-(Isopropylsulfonyl)phenyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARQE CAS No.:1105194-09-9 MDL No.:MFCD11986956 MF:C11H13N3O3S MW:267.3042 |
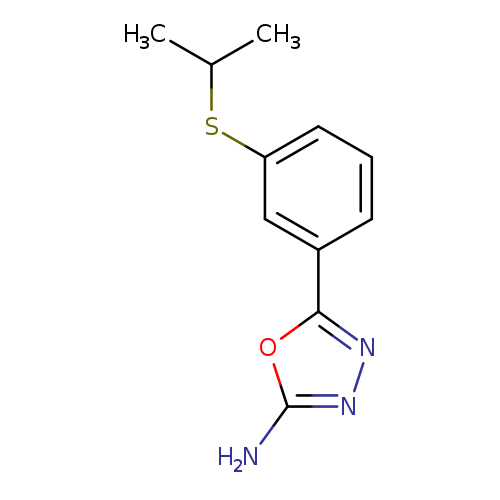
5-(3-(Isopropylthio)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA0191KG CAS No.:1105194-14-6 MDL No.:MFCD11986957 MF:C11H13N3OS MW:235.3054 |
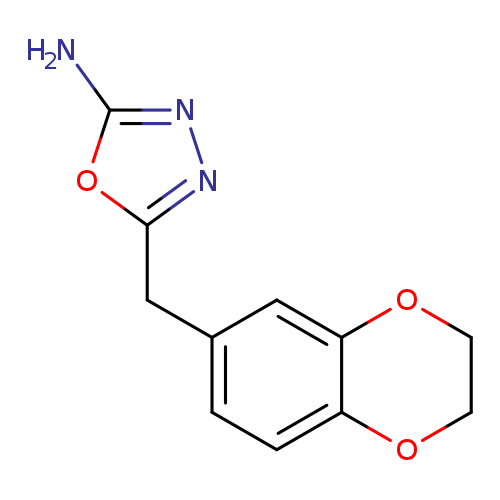
5-((2,3-Dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)methyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA0191KH CAS No.:1105194-19-1 MDL No.:MFCD11986958 MF:C11H11N3O3 MW:233.2233 |
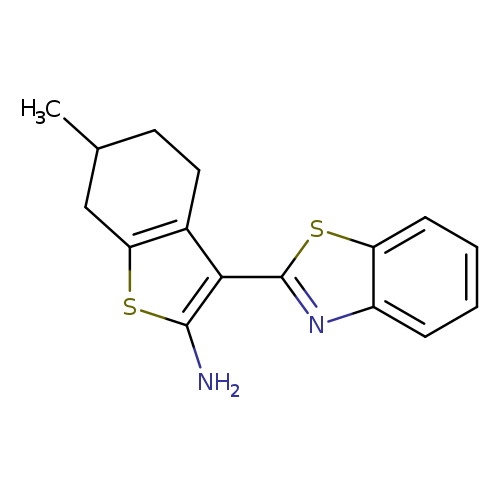
[3-(1,3-BENZOTHIAZOL-2-YL)-6-METHYL-4,5,6,7-TETRAHYDRO-1-BENZOTHIEN-2-YL]+Catalog No.:AA01ARU5 CAS No.:1105194-23-7 MDL No.:MFCD11986727 MF:C16H16N2S2 MW:300.4416 |
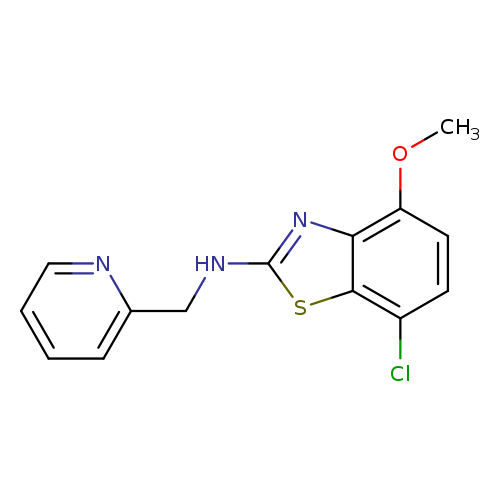
7-Chloro-4-methoxy-n-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)benzo[d]thiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01FLZR CAS No.:1105194-24-8 MDL No.:MFCD28054174 MF:C14H12ClN3OS MW:305.7826 |
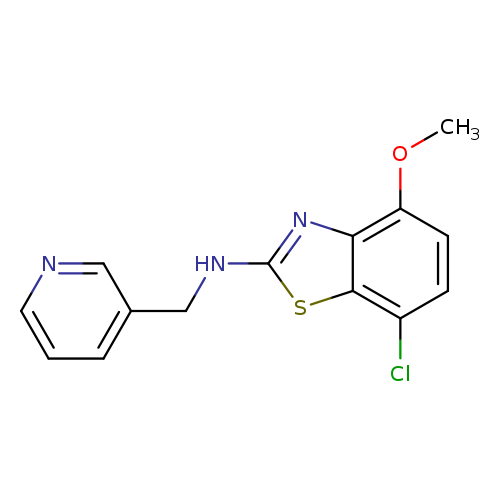
7-CHLORO-4-METHOXY-N-(PYRIDIN-3-YLMETHYL)-1,3-BENZOTHIAZOL-2-AMINECatalog No.:AA01ASAM CAS No.:1105194-29-3 MDL No.:MFCD11986960 MF:C14H12ClN3OS MW:305.7826 |
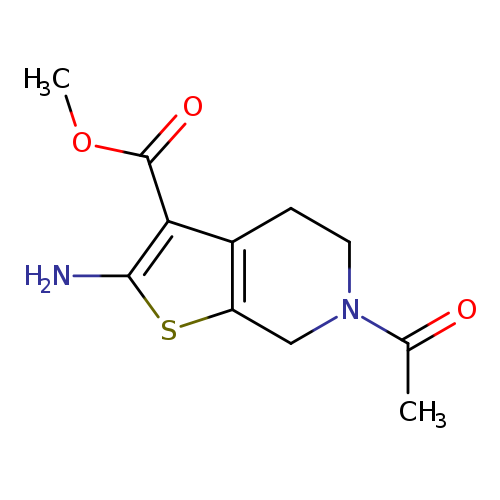
METHYL 6-ACETYL-2-AMINO-4,5,6,7-TETRAHYDROTHIENO[2,3-C]PYRIDINE-3-CARBOXY+Catalog No.:AA01ARU6 CAS No.:1105194-32-8 MDL No.:MFCD11986729 MF:C11H14N2O3S MW:254.3055 |
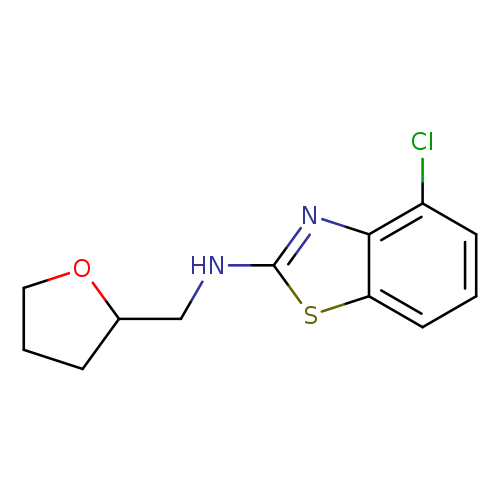
4-Chloro-n-(tetrahydrofuran-2-ylmethyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARR4 CAS No.:1105194-33-9 MDL No.:MFCD11986961 MF:C12H13ClN2OS MW:268.7624 |
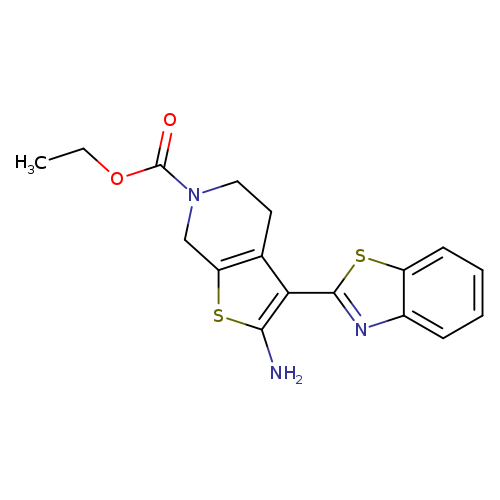
ETHYL 2-AMINO-3-(1,3-BENZOTHIAZOL-2-YL)-4,7-DIHYDROTHIENO[2,3-C]PYRIDINE-+Catalog No.:AA01ARU7 CAS No.:1105194-36-2 MDL No.:MFCD11986730 MF:C17H17N3O2S2 MW:359.4658 |
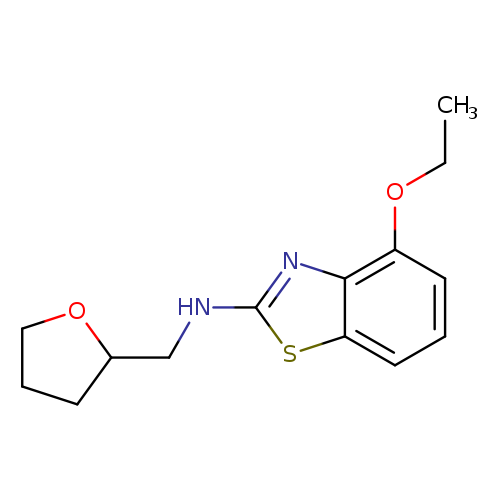
4-Ethoxy-N-(tetrahydrofuran-2-ylmethyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARRR CAS No.:1105194-37-3 MDL No.:MFCD11986962 MF:C14H18N2O2S MW:278.3699 |
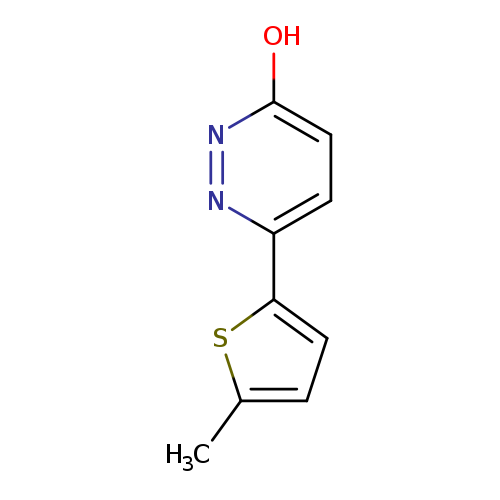
6-(5-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydropyridazin-3-oneCatalog No.:AA018BBU CAS No.:1105194-38-4 MDL No.:MFCD12143101 MF:C9H8N2OS MW:192.2376 |
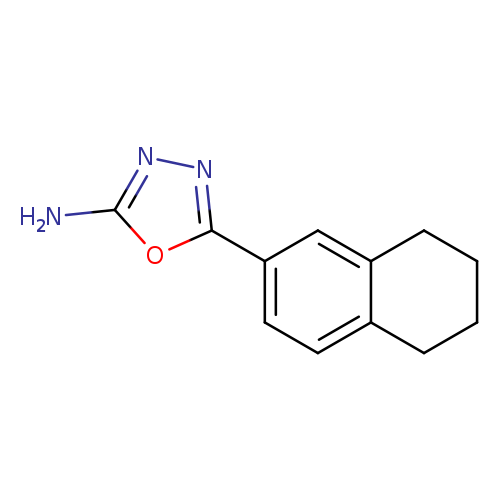
5-(5,6,7,8-Tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA00VRXW CAS No.:1105194-40-8 MDL No.:MFCD11986732 MF:C12H13N3O MW:215.2511 |
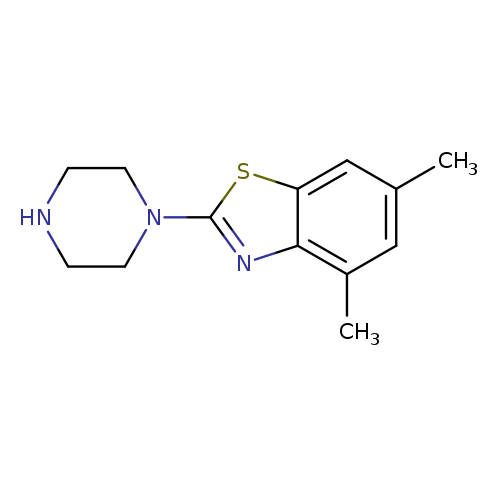
4,6-Dimethyl-2-piperazin-1-yl-1,3-benzothiazoleCatalog No.:AA01ARJ0 CAS No.:1105194-44-2 MDL No.:MFCD11986733 MF:C13H17N3S MW:247.3592 |
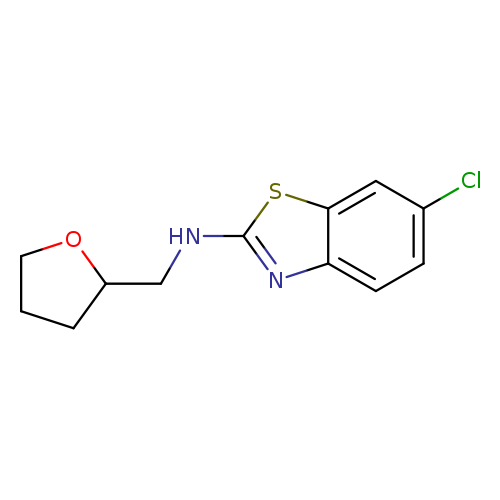
6-Chloro-N-(tetrahydrofuran-2-ylmethyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARRT CAS No.:1105194-45-3 MDL No.:MFCD11986964 MF:C12H13ClN2OS MW:268.7624 |
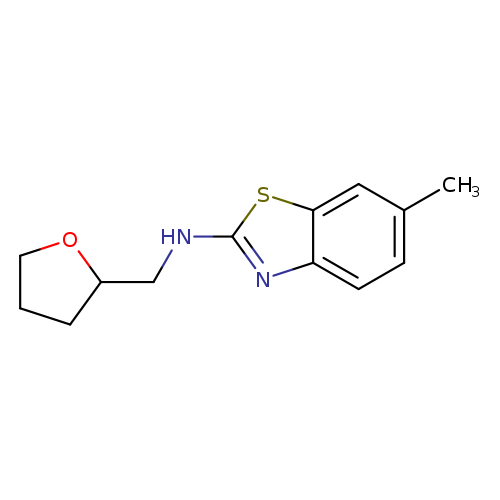
6-Methyl-N-(tetrahydrofuran-2-ylmethyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARRU CAS No.:1105194-49-7 MDL No.:MFCD11986965 MF:C13H16N2OS MW:248.3439 |
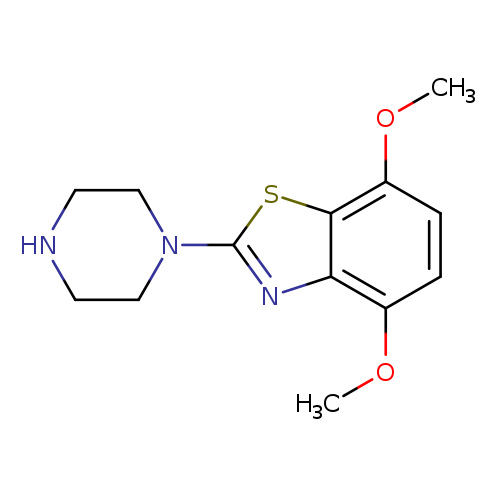
4,7-Dimethoxy-2-piperazin-1-yl-1,3-benzothiazoleCatalog No.:AA01ARJ2 CAS No.:1105194-52-2 MDL No.:MFCD11986735 MF:C13H17N3O2S MW:279.3580 |
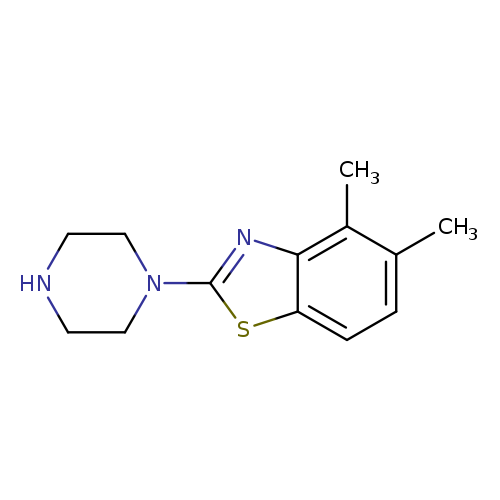
4,5-dimethyl-2-(piperazin-1-yl)benzo[d]thiazoleCatalog No.:AA01ARJP CAS No.:1105194-56-6 MDL No.:MFCD11986736 MF:C13H17N3S MW:247.3592 |
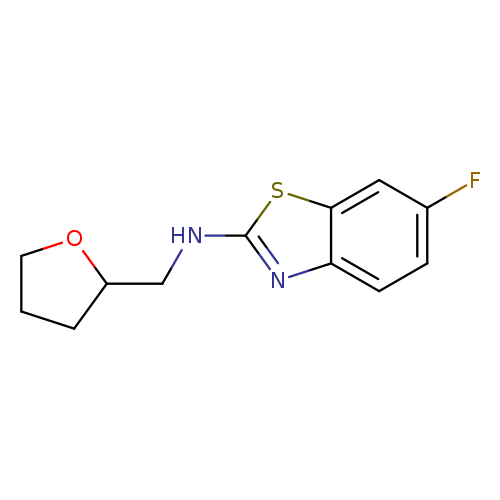
6-FLUORO-N-(TETRAHYDROFURAN-2-YLMETHYL)-1,3-BENZOTHIAZOL-2-AMINECatalog No.:AA01ARSJ CAS No.:1105194-57-7 MDL No.:MFCD11986967 MF:C12H13FN2OS MW:252.3078 |
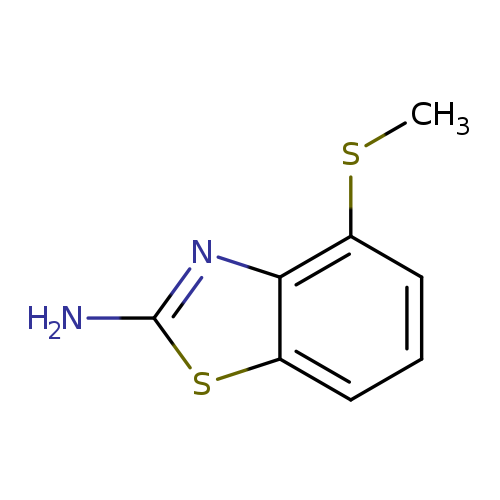
4-(methylsulfanyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARJQ CAS No.:1105194-60-2 MDL No.:MFCD11986737 MF:C8H8N2S2 MW:196.2925 |
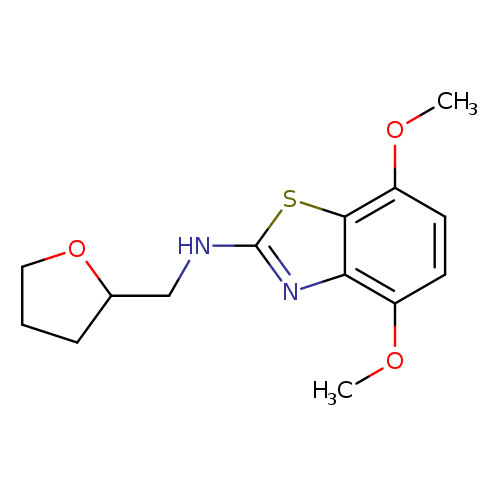
4,7-Dimethoxy-n-(tetrahydrofuran-2-ylmethyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARSK CAS No.:1105194-61-3 MDL No.:MFCD11986968 MF:C14H18N2O3S MW:294.3693 |
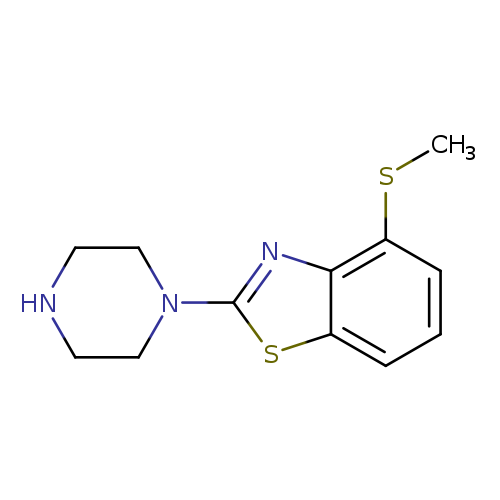
4-(Methylthio)-2-piperazin-1-yl-1,3-benzothiazoleCatalog No.:AA01ARJR CAS No.:1105194-64-6 MDL No.:MFCD11986738 MF:C12H15N3S2 MW:265.3976 |
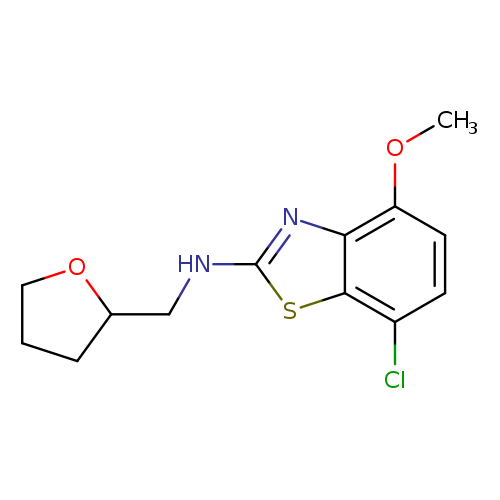
7-CHLORO-4-METHOXY-N-(TETRAHYDROFURAN-2-YLMETHYL)-1,3-BENZOTHIAZOL-2-AMIN+Catalog No.:AA01ARSL CAS No.:1105194-65-7 MDL No.:MFCD11986969 MF:C13H15ClN2O2S MW:298.7884 |
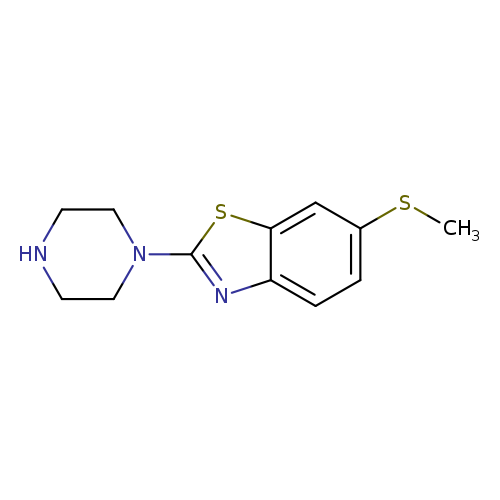
6-(Methylthio)-2-piperazin-1-yl-1,3-benzothiazoleCatalog No.:AA01ARJT CAS No.:1105194-72-6 MDL No.:MFCD11986740 MF:C12H15N3S2 MW:265.3976 |
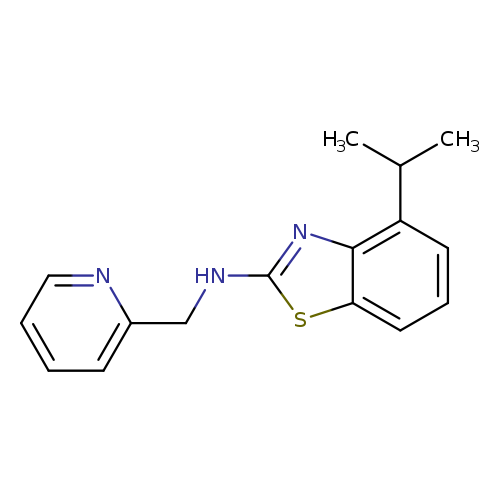
4-Isopropyl-n-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARTJ CAS No.:1105194-73-7 MDL No.:MFCD11986971 MF:C16H17N3S MW:283.3913 |
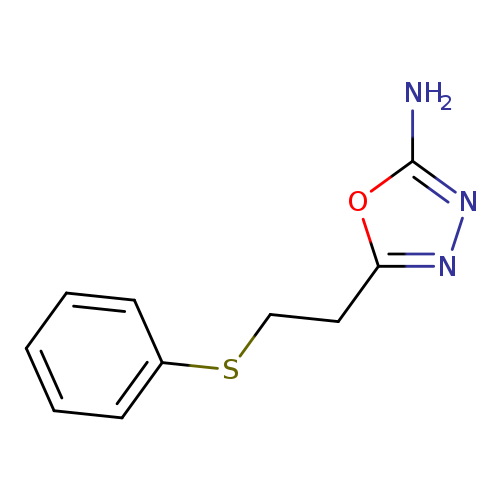
5-[2-(Phenylthio)ethyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA018GCC CAS No.:1105194-76-0 MDL No.:MFCD11986743 MF:C10H11N3OS MW:221.2788 |
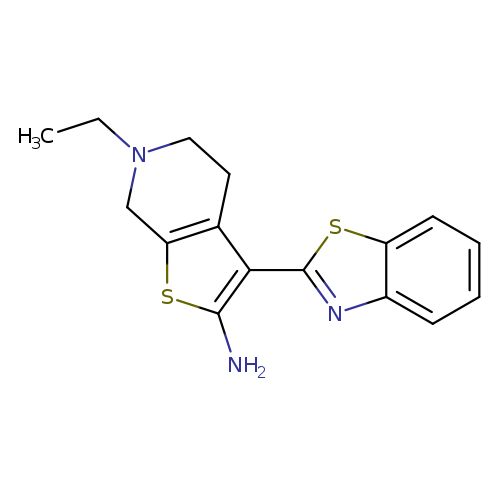
3-(1,3-BENZOTHIAZOL-2-YL)-6-ETHYL-4,5,6,7-TETRAHYDROTHIENO[2,3-C]PYRIDIN-+Catalog No.:AA01ARTK CAS No.:1105194-85-1 MDL No.:MFCD11986972 MF:C16H17N3S2 MW:315.4563 |
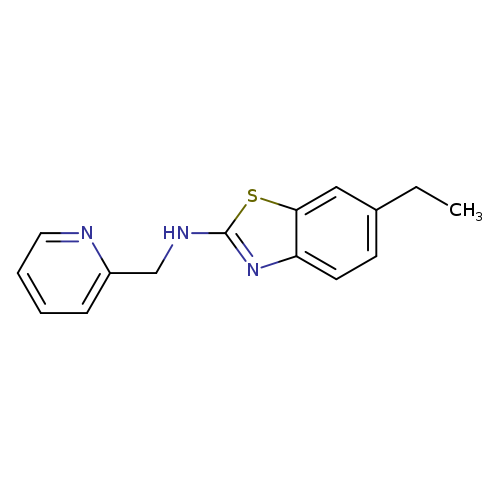
6-Ethyl-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARL5 CAS No.:1105194-88-4 MDL No.:MFCD11986747 MF:C15H15N3S MW:269.3647 |
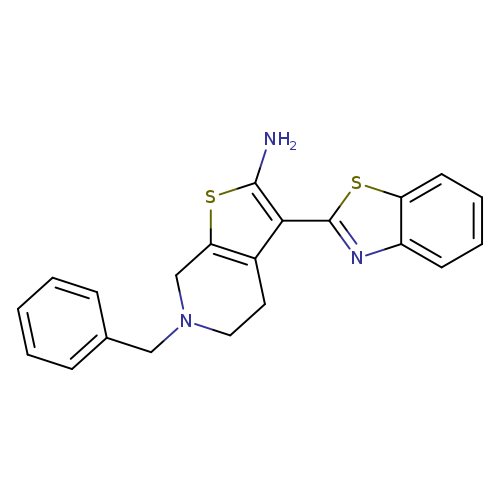
3-(1,3-Benzothiazol-2-yl)-6-benzyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]pyridin-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARTL CAS No.:1105194-89-5 MDL No.:MFCD11986973 MF:C21H19N3S2 MW:377.5257 |
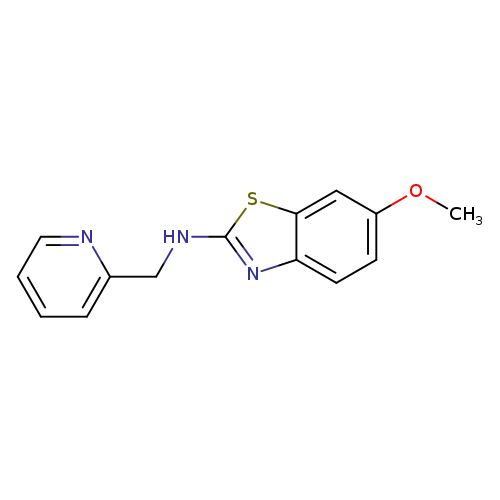
6-Methoxy-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARL6 CAS No.:1105194-92-0 MDL No.:MFCD11986748 MF:C14H13N3OS MW:271.3375 |
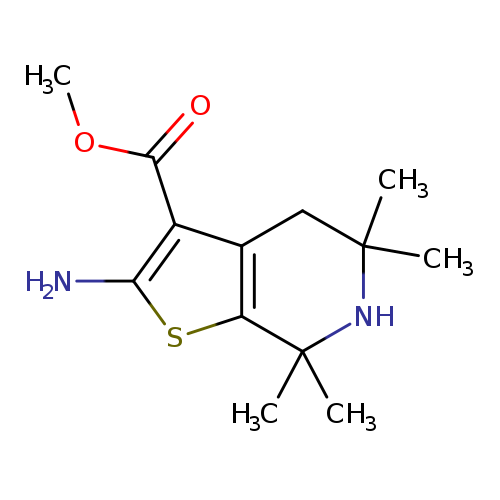
Methyl 2-amino-5,5,7,7-tetramethyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-3-carboxylateCatalog No.:AA01ARTM CAS No.:1105194-93-1 MDL No.:MFCD11986975 MF:C13H20N2O2S MW:268.3751 |
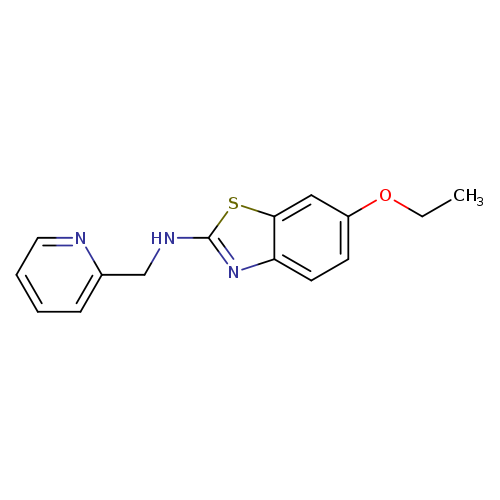
6-Ethoxy-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01FLYE CAS No.:1105194-96-4 MDL No.:MFCD11986749 MF:C15H15N3OS MW:285.3641 |
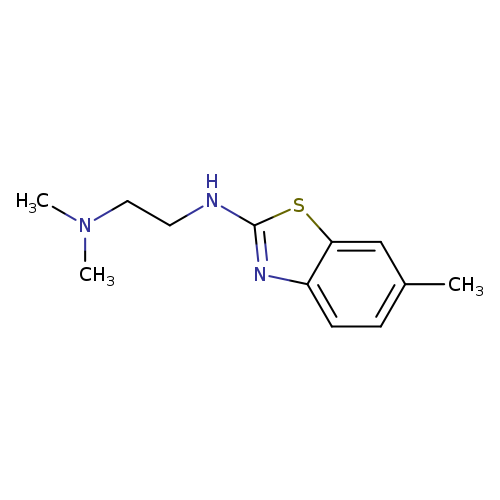
N,N-Dimethyl-N'-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)ethane-1,2-diamineCatalog No.:AA01ARUE CAS No.:1105194-97-5 MDL No.:MFCD11986976 MF:C12H17N3S MW:235.3485 |
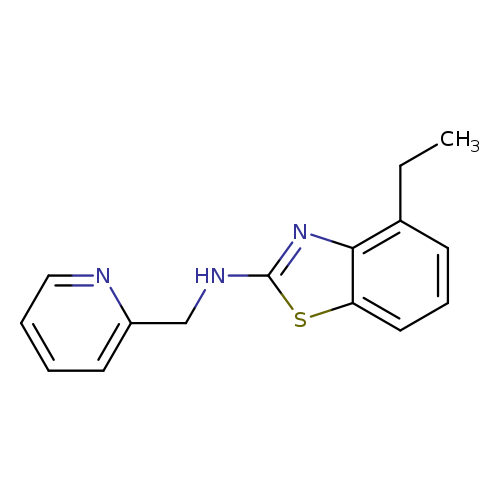
4-Ethyl-n-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01ARL7 CAS No.:1105195-00-3 MDL No.:MFCD11986750 MF:C15H15N3S MW:269.3647 |