2020-02-20 15:11:02
Lu Ding, Run-Duo Gao, and Shu-Li You
Fused indolenines are important structural cores of natural products and frequently appear in biologically active mole- cules (Figure 1).[1] Accordingly, extensive efforts have been de- voted to developing efficient methods for the construction of these scaffolds in a highly chemo- and enantioselective manner. In this regard, the recently emerging catalytic asym- metric dearomatization (CADA) reactions provide a large array of methods allowing for efficient access to fused indolenines from readily available indole derivatives.[2] Notably, transition- metal-catalyzed allylic dearomatization reactions of indoles have witnessed significant progresses in the past decade.[3,4,5] Recently, we realized the construction of fused indolenine skeletons in a cascade fashion.[6] In 2014, the Rawal group and we independently reported an intermolecular cascade dearo- matization reaction of indole-based bisnucleophiles with prop- argyl carbonate, leading to a series of spiroindolenines and spi- roindolines. Moderate enantioselectivity (, 77 % ee) was ach- ieved for limited substrates (Scheme 1, reaction 1).[6a,7,8] Rawal and co-workers found that the indole N@H moiety could par- ticipate in the cyclization process when the nucleophilic side chain was decorated at the C2 position of the C3 methyl sub- stituted indole (Scheme 1, reaction 2).[7,9] Herein, we report a chemo- and enantioselective synthesis of multisubstituted fused indolenines by Pd-catalyzed cascade dearomatization of indoles bearing a nucleophile at the C2 position with proparg- yl carbonate (Scheme 1, reaction 3).
We began our studies by examining the reaction of dimethyl 2-[(3-benzyl-1H-indol-2-yl)methyl]malonate (1 a) with methyl prop-2-yn-1-yl carbonate (2) in dimethylacetamide (DMA) in the presence of a Pd catalyst derived from Pd2dba3. Firstly, sev- eral commercially available chiral phosphorus ligands were tested (Scheme 2). The desired product 3a was obtained in moderate yields when Feringa ligand (S,S,Sa)-L1, BINAP (R)-L2, or Synphos (R)-L3 were used. However, the Pd complex de- rived from PHOX ligand (S)-L4 could hardly promote this reac- tion. It is worth noting that the reaction with L1 led to 3a in excellent enantioselectivity and good chemoselectivity (94 % ee, 10:1 3 a/4 a). Encouraged by these results, phosphora- midite ligands L5-L9 were investigated, however, no better re- sults were obtained. Next, further optimization of the reaction conditions was carried out using L1 (Table 1). Reactions in vari- ous solvents, such as DMF, CH2Cl2, and THF, afforded compara- ble yields and enantioselectivity albeit with lower 3 a/4a ratios (entries 2–4), whereas MeOH and PhMe led to almost no reac- tion (entries 5–6). Further evaluation of the concentration (entries 7–11) of 1a revealed that c = 0.2 mol L@1 was optimal in terms of yield (entry 8). Pd2(4-OMe-dba)3 was a better palladium source than Pd2dba3 and [Pd(allyl)Cl]2 (entries 12 and 13).[10] Furthermore, some additives were tested. To our delight, both yield and 3 a/4a ratio were improved remarkably when 4 a molecular sieves were used (82 % yield, 95 % ee, > 19:1 3 a/4 a, entry 15). Finally, the optimized reaction conditions were es- tablished as the following: Pd2(4-OMe-dba)3 (2.5 mol%), L1 (11 mol%), 4 a MS (100 mg) in DMA (1 mL) at 80 8C (entry 15). Notably, 4a could not be converted to 3a under the optimized conditions, suggesting the formation of C@N is likely an irreversible process here.
With the optimized conditions in hands, we then explored the substrate scope of this reaction (Scheme 3). Firstly, sub- strates with different substituents on the benzyl group were examined. Both electron-donating (3b: 4-OMe; 3c: 4-Me; 3d: 3-Me) and electron-withdrawing (3e: 4-F; 3 f: 4-Cl) groups were found to be well tolerated. The corresponding products were obtained in good to excellent yields, with excellent chemo- and enantioselectivities (3 b–3 f, 78–82 % yields, 16.2 :1 to > 19:1 3/4, 93–95 % ee). When the benzyl group was changed to 2-thienyl or 2-naphthyl, the desired products could also be obtained with gratifying re- sults (3g: 79% yield, 15.6:1 3 g/4 g, 96% ee; 3h: 85% yield, > 19:1 3 h/4 h, 96% ee). Next, substrates with different substituents on the indole ring were investi- gated. The dearomatized products were afforded in excellent yields, chemo- and enantioselectivities when an electron-donating group (3i: 5-OMe, 3j: 5- Me) was installed on the indole ring (3i: 84% yield, > 19:1 3 i/4 i, 96% ee ; 3j: 86% yield, > 19:1 3 j/4 j, 92 % ee). Remarkably, when an electron-withdrawing group was introduced on the indole ring (3k: 5-F; 3l: 5-Cl; 3m: 5-Br; 3n: 6-F; 3o: 6-Cl), good to excel- lent yields, C/N ratios and excellent enantioselectivity were obtained (3 k–3o: 73–77 % yields, 4.2:1 to 11.7:1 3/4, 92–94 % ee). Notably, the formation of al- lylic amination products was more favorable when stronger electron-withdrawing group was introduced (from 5-F to 5-Br, 6-F to 6-Cl). These are probably due to the increased acidity of the indole N@H and more easily formed N nucleophiles caused by the electron-withdrawing substituent. When the elec- tron-withdrawing group on substrate 1 was changed from methyl carbonate to ethyl carbonate, the desired product could also be obtained in good results (3p: 71% yield, 18.3 :1 3 p/4 p, 91% ee). Furthermore, when an aliphatic group was in- stalled at the C3 position, all substrates were well tolerated (3 q–3v: 71–85 % yields, > 19:1 3/4 in all cases, 92–94 % ee). The structure and absolute configuration of product 3r were confirmed by an X-ray crystallographic analysis of an enantio- pure example (see the Supporting Information for details). Moreover, substrate 1w bearing a nucleophilic chain at the C3 position underwent the reaction smoothly, affording the bridged indoline 3w in 71 % yield and 96 % ee.
To demonstrate the utility of the current method, a gram-scale reaction and several transformations of the product were carried out (Scheme 4). The asymmetric cascade dearomatization reaction of 1a with 2 on a 3.0 mmol scale provided product 3a in 84 % yield and 95 % ee. Under Pd/C hydrogena- tion conditions, the exocyclic double bond of product 3a was reduced and the benzyl group was also removed at the same time likely due to the driving force of aromatiza- tion, giving 5 in 92 % yield. The imine moiety in 3a could be reduced by NaBH3CN in acetic acid to afford 6 in 91 % yield. The relative configuration of 6 was determined by NOE analysis (for details, see the Sup- porting Information). Treatment of 6 with acetyl chloride and NaH produced 7 in quantitative yield. Finally, the double bond in 7 was oxidized with ozone to give ketone 8 in 64 % yield.
A proposed catalytic cycle is depicted in Scheme 5. The propargyl carbonate is acti- vated by Pd0 to give intermediate. Then, the nucleophilic side chain attacks intermediate to generate p-allyl palladium species. Upon the deprotonation of indole N@H, the C3 position of indole in III attacks p-allyl palla- dium moiety to deliver IV. Finally, product 3 is provided upon the liberation of palladium catalyst.
In conclusion, we have achieved an efficient palladium(0)-catalyzed intermolecular asymmetric cascade dearomatization reac- tion of indole derivatives with propargyl car- bonate. A series of multiply substituted fused indolenines were obtained in good to excellent yields, excellent chemo- and enan- tioselectivities. This method features mild reaction conditions and broad substrate scope. Further studies on the reaction mechanism are currently underway in our laboratory.
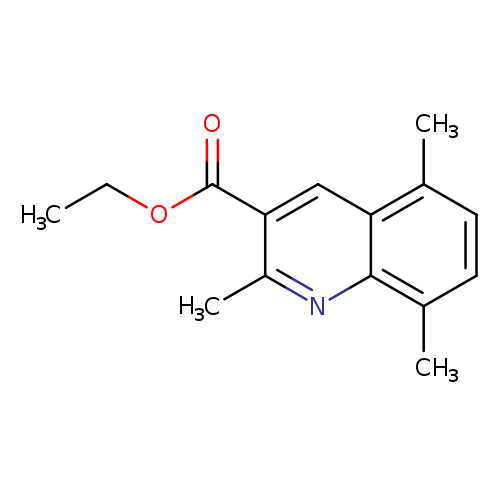
2,5,8-Trimethylquinoline-3-carboxylic acid ethyl esterCatalog No.:AA0092Y5 CAS No.:110139-48-5 MDL No.:MFCD09787534 MF:C15H17NO2 MW:243.3010 |
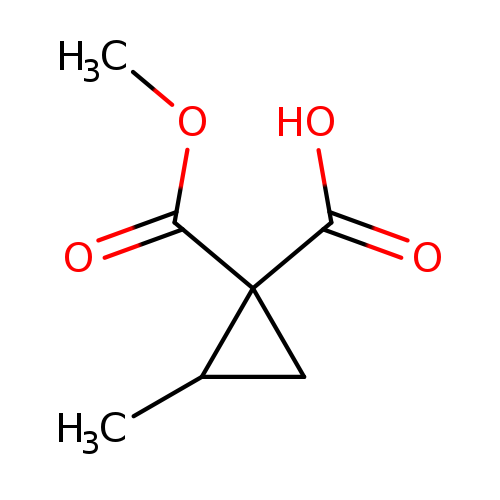
1-(METHOXYCARBONYL)-2-METHYLCYCLOPROPANE-1-CARBOXYLIC ACIDCatalog No.:AA01EK2S CAS No.:1101485-17-9 MDL No.:MFCD24499992 MF:C7H10O4 MW:158.1519 |
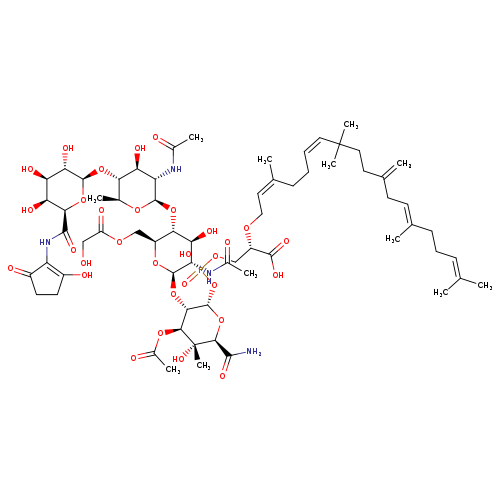
BambermycinCatalog No.:AA01DQ75 CAS No.:11015-37-5 MDL No.:MFCD01742468 MF:C66H101N4O31P MW:1477.4901 |

C-PHYCOCYANINCatalog No.:AA008R6R CAS No.:11016-15-2 MDL No.:MFCD00130691 MF: MW: |
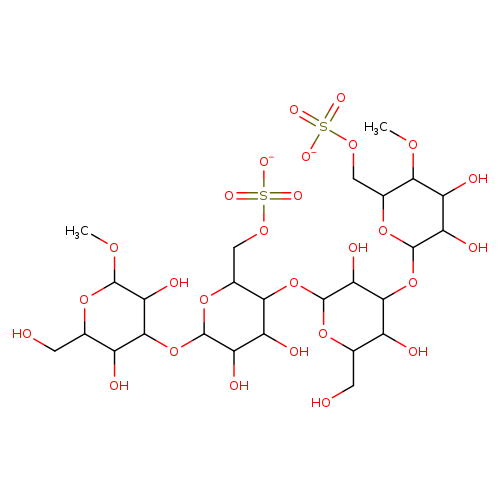
porphyranCatalog No.:AA009RFD CAS No.:11016-36-7 MDL No.: MF:C26H44O27S2-- MW:852.7414 |
Proparyl-peg5-methaneCatalog No.:AA00HBLS CAS No.:1101668-39-6 MDL No.:MFCD06796762 MF:C12H22O5 MW:246.3001 |
(4-Benzylmorpholin-3-yl)methanolCatalog No.:AA003SOH CAS No.:110167-20-9 MDL No.:MFCD04038651 MF:C12H17NO2 MW:207.2689 |
(3-Furan-2-yl-5-thioxo-1,5-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazol-4-yl)-acetic acidCatalog No.:AA008SJ4 CAS No.:110167-66-3 MDL No.:MFCD08437536 MF:C8H7N3O3S MW:225.2245 |
((3-Fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)prolineCatalog No.:AA01FLV7 CAS No.:1101743-81-0 MDL No.:MFCD07433698 MF:C11H12FNO4S MW:273.2807 |
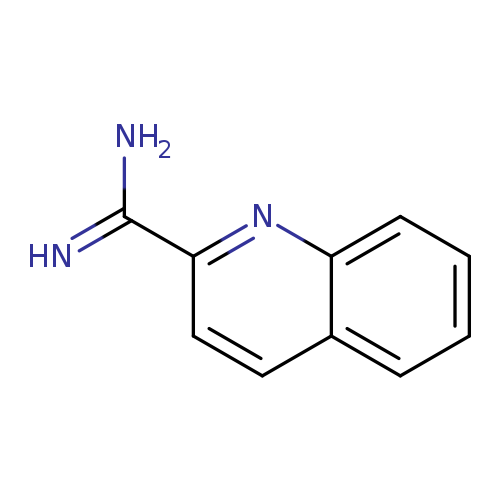
Quinoline-2-carboximidamide hydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA008ZT2 CAS No.:110177-05-4 MDL No.:MFCD08752296 MF:C10H9N3 MW:171.1986 |
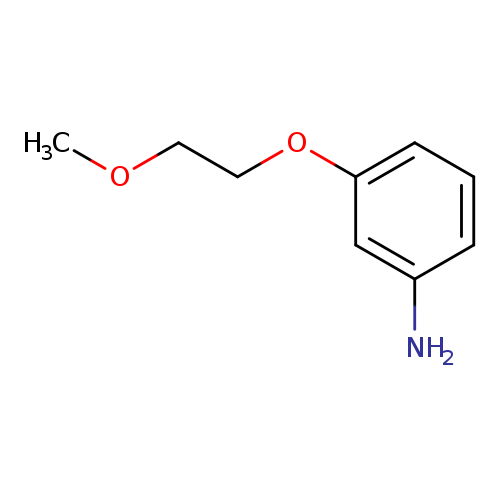
3-(2-Methoxyethoxy)anilineCatalog No.:AA007VO1 CAS No.:110178-35-3 MDL No.:MFCD08691445 MF:C9H13NO2 MW:167.2050 |
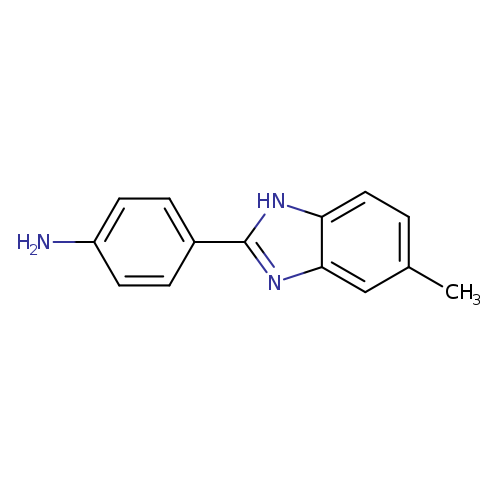
4-(5-Methyl-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)anilineCatalog No.:AA007VO0 CAS No.:110178-74-0 MDL No.:MFCD00628968 MF:C14H13N3 MW:223.2731 |
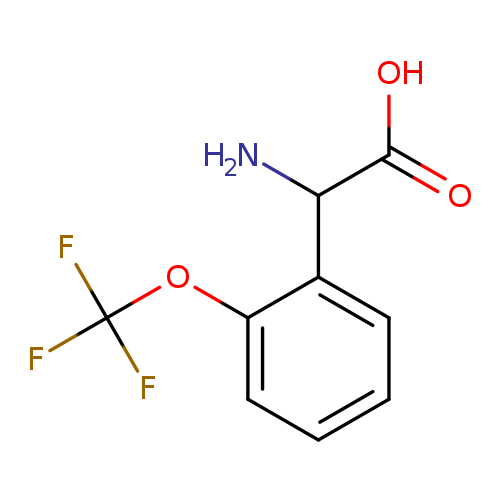
2-Amino-2-(2-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)acetic acidCatalog No.:AA007VO2 CAS No.:1101781-50-3 MDL No.:MFCD07371767 MF:C9H8F3NO3 MW:235.1599 |
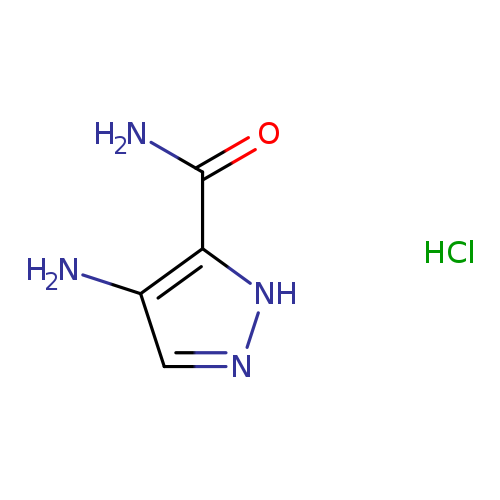
4-Amino-1h-pyrazole-5-carboxamide hydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA00J21Z CAS No.:1101785-22-1 MDL No.:MFCD18071213 MF:C4H7ClN4O MW:162.5776 |
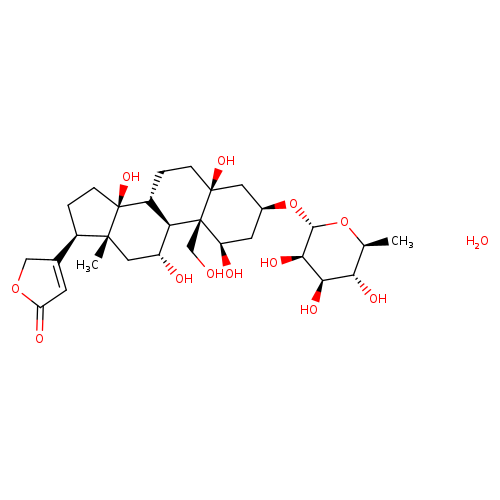
OUABAIN OCTAHYDRATECatalog No.:AA008RAU CAS No.:11018-89-6 MDL No.:MFCD00149240 MF:C29H46O13 MW:602.6677 |
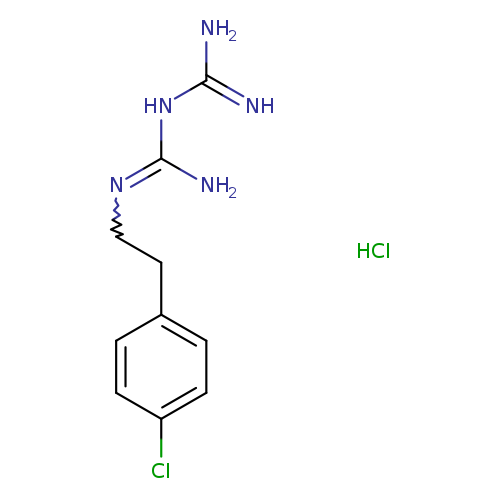
2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]carbamimidamidomethanimidamide hydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA01BBH4 CAS No.:110181-28-7 MDL No.:MFCD28506029 MF:C10H15Cl2N5 MW:276.1656 |
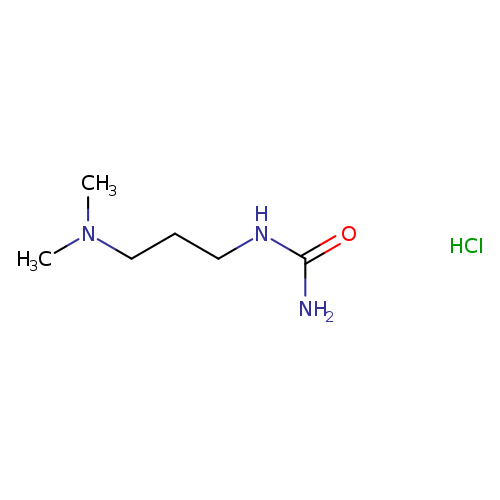
[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]urea hydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA01A7QP CAS No.:110181-34-5 MDL No.:MFCD14705818 MF:C6H16ClN3O MW:181.6637 |
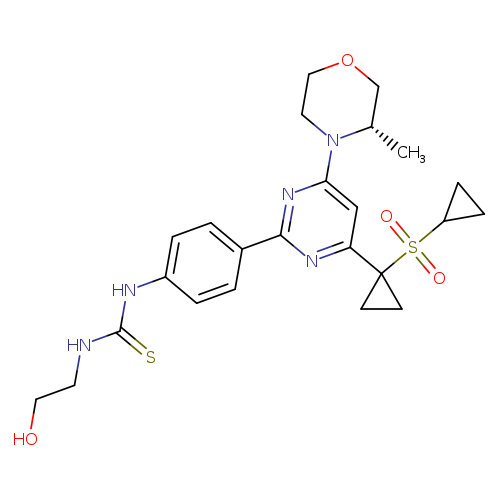
N-[4-[4-[1-(cyclopropylsulfonyl)cyclopropyl]-6-[(3S)-3-methyl-4-morpholinyl]-2-pyrimidinyl]phenyl]-N'-(2-hydroxyethyl)-thioureaCatalog No.:AA01EPNU CAS No.:1101810-02-9 MDL No.:MFCD28411426 MF:C24H31N5O4S2 MW:517.6640 |
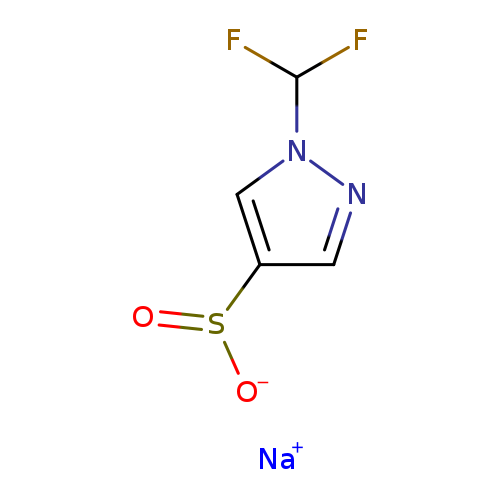
Sodium 1-(difluoromethyl)-1h-pyrazole-4-sulfinateCatalog No.:AA01EK20 CAS No.:1101821-28-6 MDL No.:MFCD28404486 MF:C4H3F2N2NaO2S MW:204.1304 |
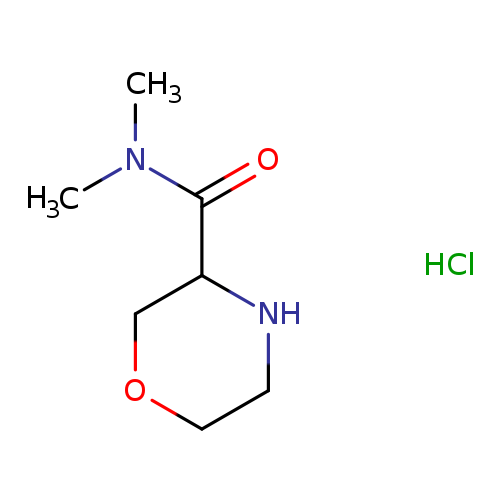
N,N-dimethylmorpholine-3-carboxamide hydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA01EIZH CAS No.:1101822-35-8 MDL No.:MFCD31617414 MF:C7H15ClN2O2 MW:194.6592 |
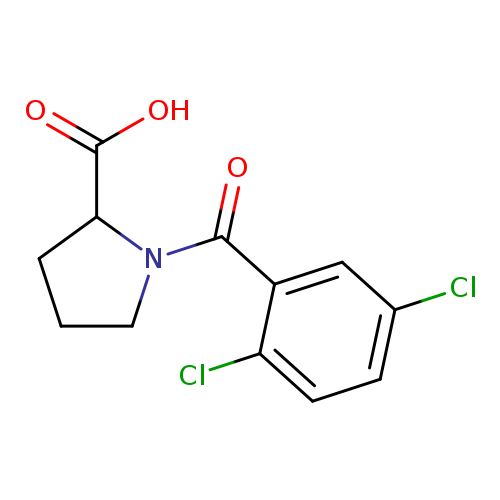
1-(2,5-dichlorobenzoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA01EKF4 CAS No.:1101837-02-8 MDL No.:MFCD09805454 MF:C12H11Cl2NO3 MW:288.1266 |
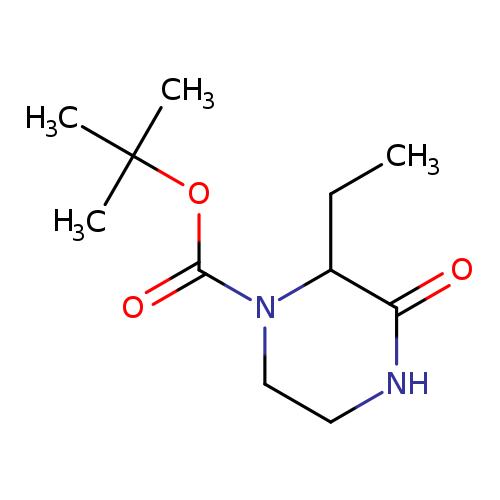
tert-butyl 2-ethyl-3-oxopiperazine-1-carboxylateCatalog No.:AA01ABDU CAS No.:1101840-55-4 MDL No.:MFCD18845686 MF:C11H20N2O3 MW:228.2881 |
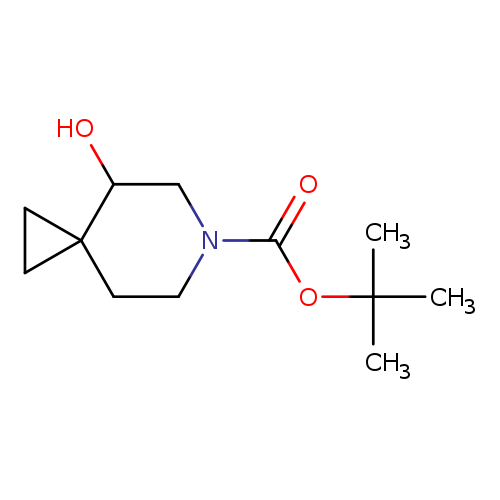
tert-Butyl 4-hydroxy-6-azaspiro[2.5]octane-6-carboxylateCatalog No.:AA00971I CAS No.:1101840-72-5 MDL No.:MFCD22741890 MF:C12H21NO3 MW:227.3000 |
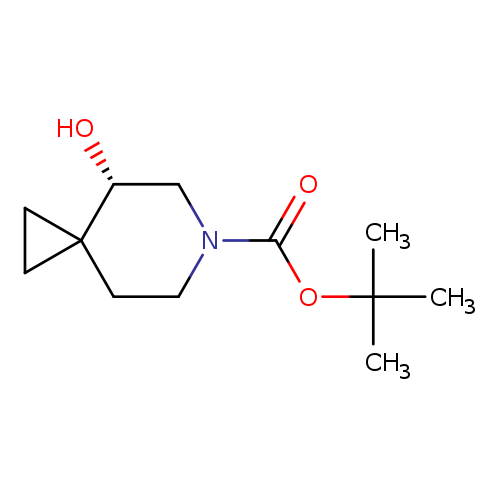
6-Azaspiro[2.5]octane-6-carboxylic acid, 4-hydroxy-, 1,1-dimethylethyl ester, (4S)-Catalog No.:AA00IKR7 CAS No.:1101840-73-6 MDL No.:MFCD22741891 MF:C12H21NO3 MW:227.3000 |
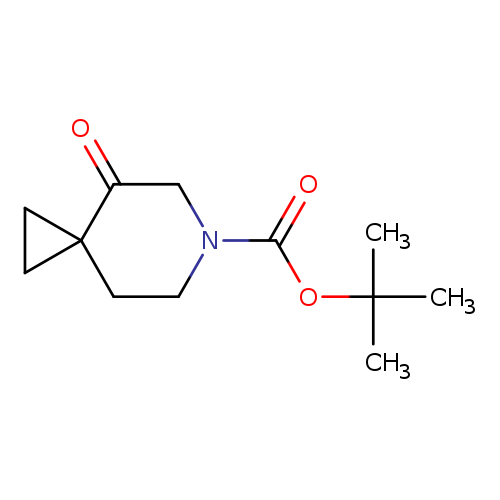
tert-Butyl 4-oxo-6-azaspiro[2.5]octane-6-carboxylateCatalog No.:AA00HBLY CAS No.:1101840-74-7 MDL No.:MFCD21607170 MF:C12H19NO3 MW:225.2842 |
1-[2-(difluoromethoxy)benzoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA01EKFN CAS No.:1101842-37-8 MDL No.:MFCD02339988 MF:C13H13F2NO4 MW:285.2434 |
1-(3-methyl-4-nitrobenzoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA01EKGK CAS No.:1101842-87-8 MDL No.:MFCD09807085 MF:C13H14N2O5 MW:278.2607 |
Methyl jasmonateCatalog No.:AA008WR6 CAS No.:1101843-02-0 MDL No.:MFCD00036656 MF:C13H20O3 MW:224.2961 |
1-Butanoylpiperidine-2-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA00HBLZ CAS No.:1101848-24-1 MDL No.:MFCD09813230 MF:C10H17NO3 MW:199.2469 |
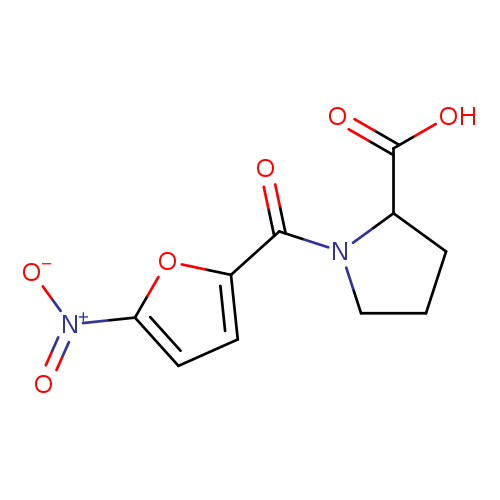
1-[(5-Nitrofuran-2-yl)carbonyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA01EKF8 CAS No.:1101848-43-4 MDL No.:MFCD09814024 MF:C10H10N2O6 MW:254.1962 |
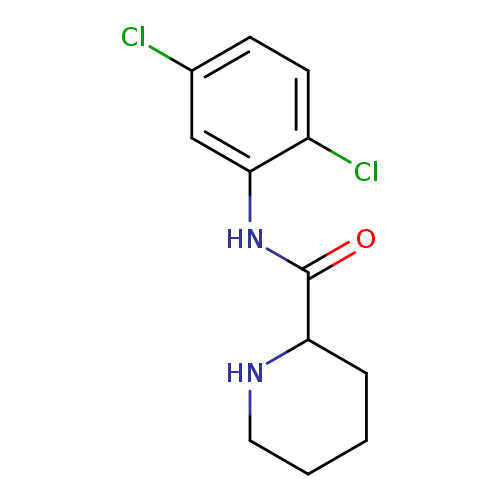
N-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamideCatalog No.:AA019MD5 CAS No.:1101852-03-2 MDL No.:MFCD09816528 MF:C12H14Cl2N2O MW:273.1584 |
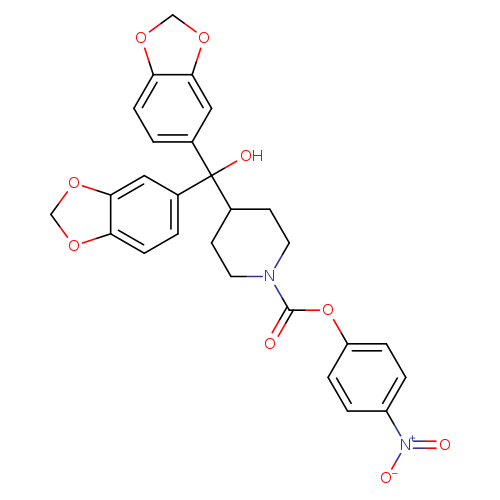
JZL 184Catalog No.:AA008SP8 CAS No.:1101854-58-3 MDL No.:MFCD11976911 MF:C27H24N2O9 MW:520.4875 |
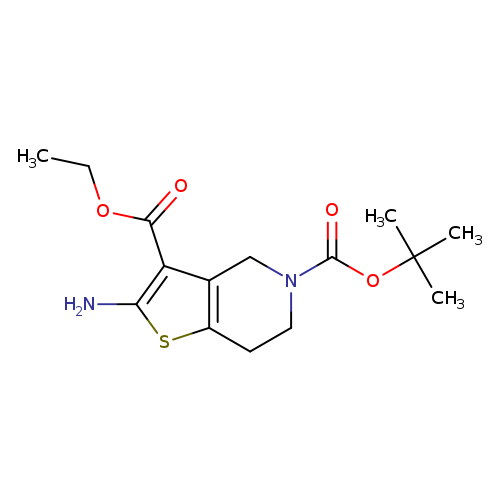
Ethyl 2-amino-5-boc-6,7-dihydro-4h-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-3-carboxylateCatalog No.:AA00HBM1 CAS No.:1101856-88-5 MDL No.:MFCD23105852 MF:C15H22N2O4S MW:326.4112 |
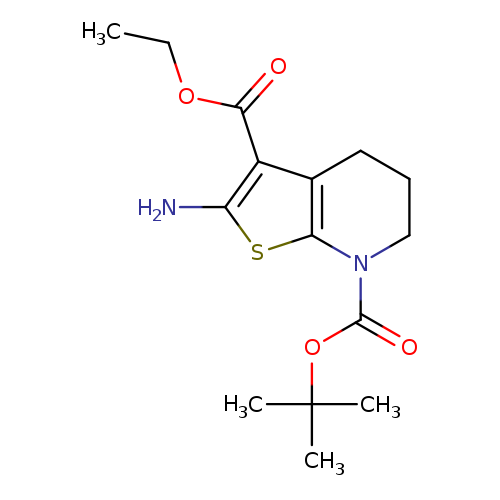
Thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-3,7(4H)-dicarboxylic acid, 2-amino-5,6-dihydro-, 7-(1,1-dimethylethyl) 3-ethyl esterCatalog No.:AA00IL2Z CAS No.:1101857-21-9 MDL No.:MFCD31617933 MF:C15H22N2O4S MW:326.4112 |
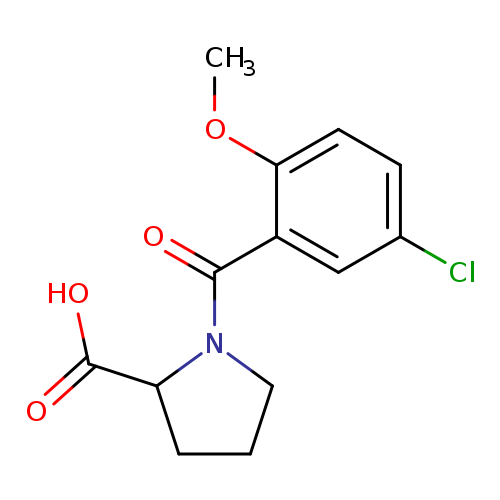
1-(5-Chloro-2-methoxybenzoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA01EKFZ CAS No.:1101860-80-3 MDL No.:MFCD09812458 MF:C13H14ClNO4 MW:283.7076 |
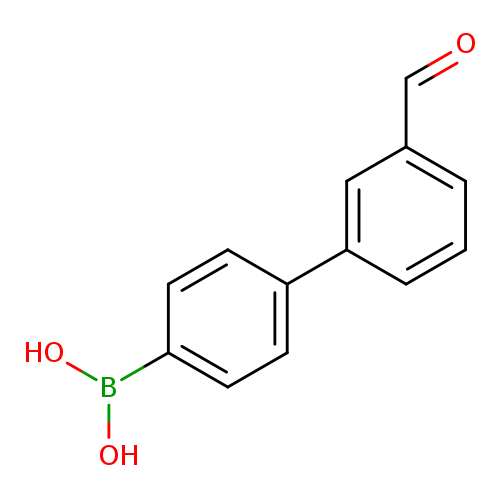
4-(3-Formylphenyl)phenylboronic acidCatalog No.:AA00HBM3 CAS No.:1101866-02-7 MDL No.:MFCD08701745 MF:C13H11BO3 MW:226.0356 |
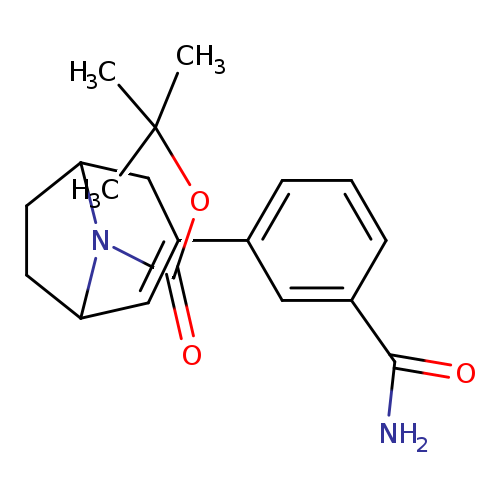
tert-Butyl 3-(3-carbamoylphenyl)-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-2-ene-8-carboxylateCatalog No.:AA00HBM5 CAS No.:1101869-79-7 MDL No.:MFCD28133428 MF:C19H24N2O3 MW:328.4055 |
D-Glucose-13c6Catalog No.:AA008SJZ CAS No.:110187-42-3 MDL No.:MFCD00037544 MF:C6H12O6 MW:186.1118 |
1,2-Diiodo-4,5-dimethoxybenzeneCatalog No.:AA008R5E CAS No.:110190-08-4 MDL No.:MFCD00094489 MF:C8H8I2O2 MW:389.9569 |
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-ol hydrobromideCatalog No.:AA00846S CAS No.:110192-19-3 MDL No.:MFCD12197401 MF:C9H12BrNO MW:230.1017 |
Benzene, 1-fluoro-2-iodo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-Catalog No.:AA00HBM6 CAS No.:110192-48-8 MDL No.:MFCD09800715 MF:C7H3F4I MW:289.9968 |
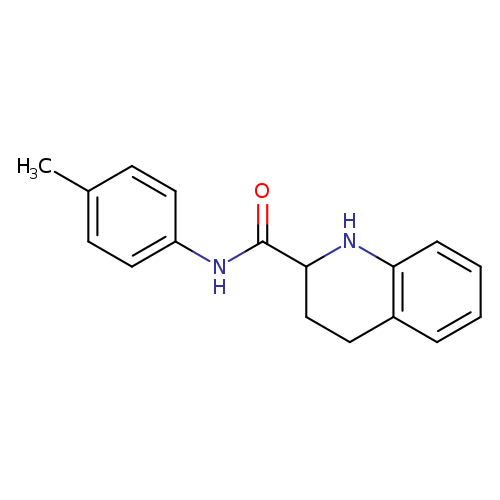
N-(4-Methylphenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-2-carboxamideCatalog No.:AA01A8ZW CAS No.:1101927-54-1 MDL No.:MFCD09935095 MF:C17H18N2O MW:266.3376 |
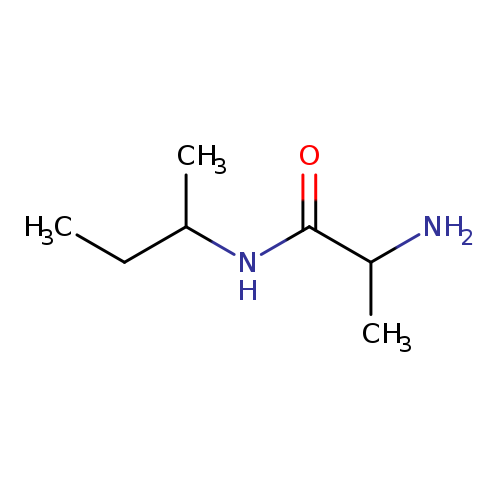
2-amino-N-(butan-2-yl)propanamideCatalog No.:AA01A7GS CAS No.:1101928-01-1 MDL No.:MFCD09937270 MF:C7H16N2O MW:144.2147 |
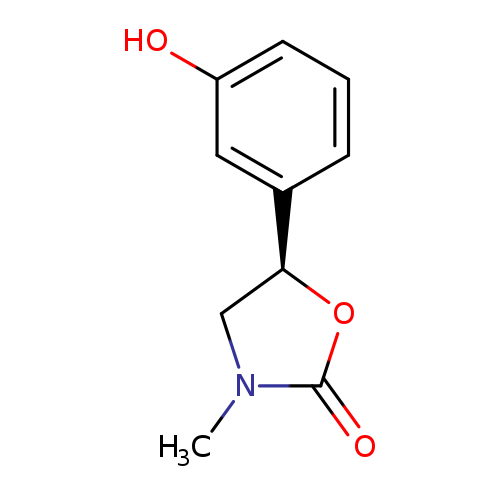
2-Oxazolidinone,5-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-, (R)- (9CI)Catalog No.:AA007VDO CAS No.:110193-49-2 MDL No.:MFCD16251422 MF:C10H11NO3 MW:193.1992 |
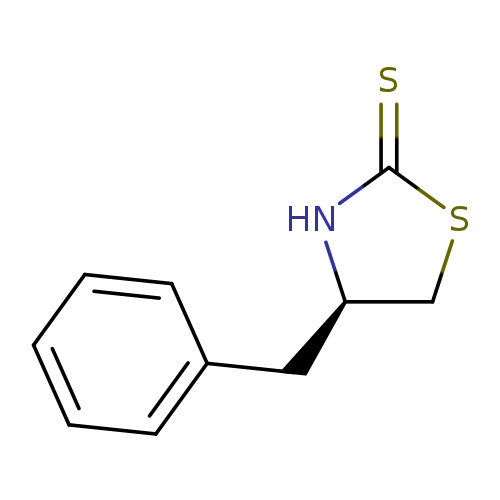
(R)-4-Benzyl-1,3-thiazolidine-2-thioneCatalog No.:AA003C7F CAS No.:110199-17-2 MDL No.:MFCD06658217 MF:C10H11NS2 MW:209.3310 |
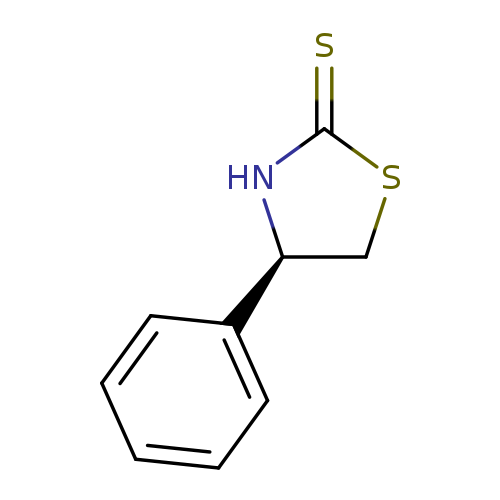
(R)-4-Phenylthiazolidine-2-thioneCatalog No.:AA008SCI CAS No.:110199-18-3 MDL No.:MFCD06658215 MF:C9H9NS2 MW:195.3045 |
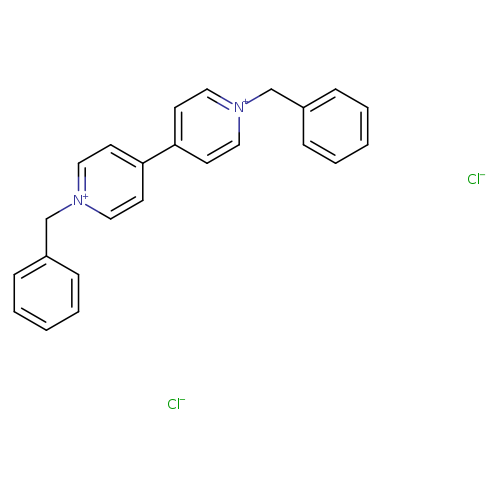
1,1'-Dibenzyl-4,4'-bipyridinium dichloride hydrateCatalog No.:AA003D5B CAS No.:1102-19-8 MDL No.:MFCD09998204 MF:C24H22Cl2N2 MW:409.3509 |
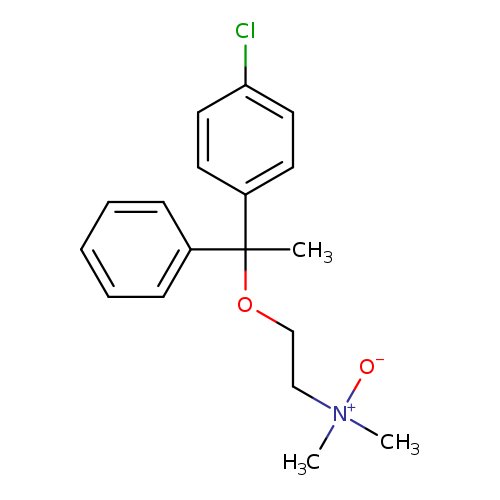
2-[1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1-phenylethoxy]-n,n-dimethylethanamine oxideCatalog No.:AA01DSSN CAS No.:110203-91-3 MDL No.:MFCD29924031 MF:C18H22ClNO2 MW:319.8258 |
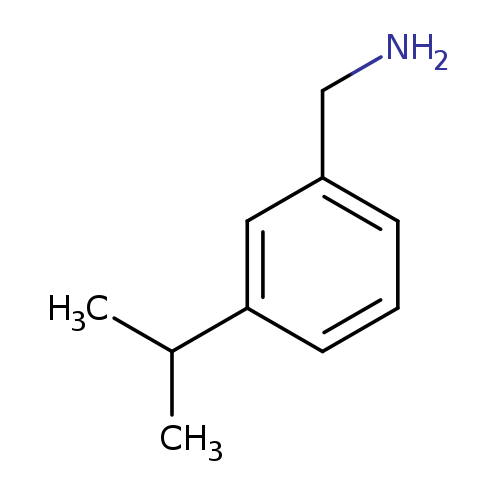
[3-(propan-2-yl)phenyl]methanamineCatalog No.:AA01ACXX CAS No.:110207-94-8 MDL No.:MFCD19541078 MF:C10H15N MW:149.2328 |
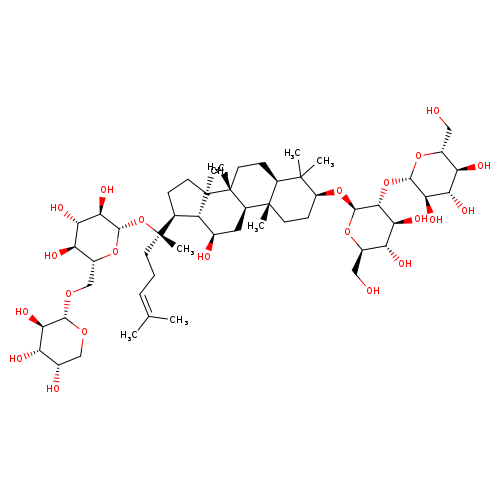
GINSENOSIDE RB2Catalog No.:AA008R0T CAS No.:11021-13-9 MDL No.:MFCD00221755 MF:C53H90O22 MW:1079.2685 |
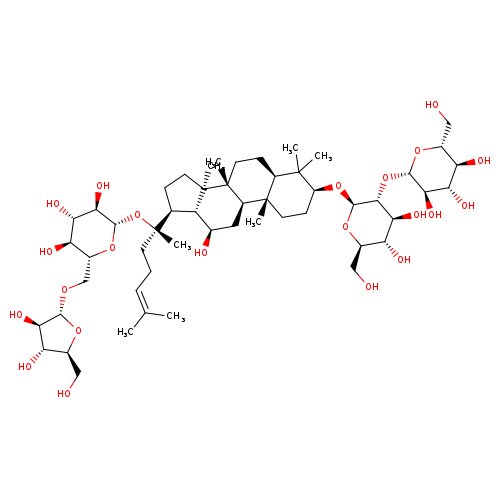
Ginsenoside rcCatalog No.:AA008R9D CAS No.:11021-14-0 MDL No.:MFCD00133368 MF:C53H90O22 MW:1079.2685 |
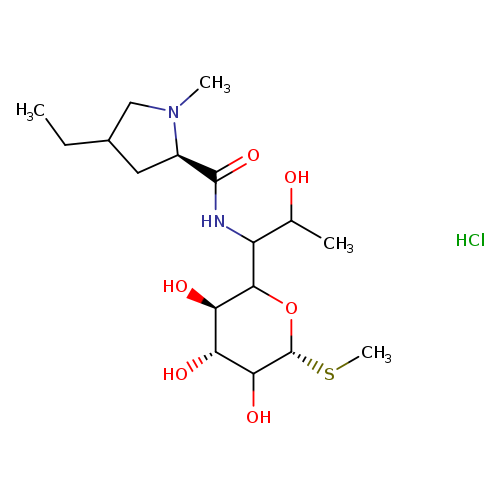
Lincomycin B HydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA008W6A CAS No.:11021-35-5 MDL No.:MFCD24386415 MF:C17H33ClN2O6S MW:428.9717 |