2019-12-30 09:04:17
Ying‐Chun Gu1* | Ren‐Ming Hu2* | Ming‐Ming Li2 | Da‐Zhen Xu
1 | INTRODUCTION
Indole derivatives are widespread in nature products.[1] Most of the known bioactive alkaloids are based on the indole moiety. They often display a wide variety of pharmacological and biological activities.[2] Among them, the densely C3‐substituted indoles have become a privileged structure in numerous research.[3,4] In particular, the bis‐indoles have attracted much attention due to their biological efficacies.[5,6] Recently, they are also used as tranquilizers in the treatment of cancer and shown to exhibit anticancer activity, inhibit the growth of cancer cells.[7] Some of the naturally occurring bioactive C3‐substituted indoles are shown in Figure 1. Moreover, C3‐substituted indoles are often employed as the key intermediates and useful building blocks in the total synthesis of natural products.[8]
Therefore, various methods have been reported for preparing this class of compounds.[9–11] The most straightforward method to obtain the heterocycle involves the condensation of indoles with different carbonyl compounds (aldehydes or ketones), which was often promoted by homo‐ and heterogeneous catalysts such as acid catalysts,[12–24] nano catalysts,[25–31] supported catalysts,[32–41] metal catalysts,ion exchange resin,[50] and enzymes.[51] Although these reported protocols have made some certain merits, many of them still have notable disadvantages such as harsh reaction conditions, long reaction times, limited substrate scope, using expensive Lewis acids and solvents, high catalyst loading and generation of large amounts of harmful wastes. Hence, the development of a new, efficient and
eco‐friendly high‐yielding general route for the synthesis of diverse C3‐substituted indole is still highly desirable.
Ionic liquid (ILs) as green media in chemical and biochemical transformations have received much attention in the last decade. Especially as environmentally friendly catalysts,[52–56] they have been successfully applied in the synthesis of densely substituted indole derivatives. However, only few literatures have mentioned the methods to obtain the trisindoline and its derivatives which were formed by the Friedel–Crafts reaction between 1 eq. isatin and 2 eq. indoles.[57–60] Even though, these methods still suffered from various disadvantages such as high reaction temperature, large amounts of catalyst loading and limited substrate scope. Recently, magnetic ILs as a new kind of ionic liquid have been proposed and introduced in a number of important organic process due to their unique characteristics.[61–73] Herein, as our ongoing interest in highly efficient ILs catalyzed multi‐component reactions,[74–79] we wish to report a new kind of magnetic IL [Dabco‐C2OH][FeCl4] as a highly efficient and recyclable catalyst for general synthesis of densely substituted indoles, including both trisindolines and bis(3‐indolyl) methanes, in excellent yields under mild conditions.
2 | RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Four IL catalysts base on the skeleton of 1,4‐diazobicyclo [2.2.2] octane (DABCO) have been synthesized, and they are shown in Figure 2. The ILs of [Dabco‐C4] Cl, [Dabco‐ C3OH] Cl, [Dabco‐C2OH] Cl, were prepared according to the standard procedure that we have reported.[75] The IL [Dabco‐C2OH][FeCl4] was easily prepared by the simple mixing [Dabco‐C2OH] Cl with FeCl3, and the anion of the catalyst Cl− was changed to FeCl4−.
The Raman spectra of [Dabco‐C2OH][FeCl4] and [Dabco‐C2OH] Cl were shown in Figure 3. The absorption bands of [Dabco‐C2OH][FeCl4] are similar to those of [Dabco‐C2OH]Cl. The [Dabco‐C2OH][FeCl4] spectrum shows one clean peak at 338 cm−1 that has been previously assigned to tetrahedral FeCl4−.[80]
Our investigation commenced with the reaction between indole (1a) and isatin (2a) in the presence of a catalytic amount of [Dabco‐C4] Cl in C2H5OH at 50 °C, and we were pleased to find that trisindoline 3a was formed in 59% yield within 6 hours (Table 1, entry 1). Then other Dabco‐based IL catalysts were tested in order to find the best catalyst for this transformation. As can be seen from the results summarized in Table 1 (entries 1–4), all the Dabco‐based IL catalysts could drive the reaction and afforded product 3a in moderate to excellent yields.
Especially in the presence of [Dabco‐C2OH][FeCl4] (10 mol%), trisindoline 3a was obtained in a fairly good yield of 98% within only 15 min (Table 1, entry 4). Even performed the reaction under near room temperature (30 °C), the product of 3a was also formed in a high yield of 96% in 50 minutes (Table 1, entry 5). To further improve the reaction conditions, different solvents, such as THF, H2O and DMF, were screened, but no better results were obtained (Table 1, entries 6–8). Next, we tried to reduce the catalytic loading to 5 mol% and 3 mol%, pruduct 3a was also formed in good yields (Table 1, entries 9 and 10).
Other catalysts, such as FeCl3 and DABCO, were also investigated, but they did not lead to better results (Table 1, entries 11 and 12). In addition, no reaction occurred even after a long reaction time when the reaction performed under condition without any catalyst (Table 1, entry 13). In order to show the efficiency of this method, we performed the reaction on 5‐mmol scale, and 1.72 g of 3a was prepared in 95% yield (Table 1, entry 14).
In order to show the merit of this work, the result regarding the reaction of indole and isatin was compared with the reported methods that are promoted by IL catalysts. As shown in Table 2, even a low amount of 5 mol% [Dabco‐C2OH][FeCl4] could also drive the reaction to afford corresponding product 3a in an excellent yield within a very short time (Table 1, entry 5). All the results indicated that the IL [Dabco‐C2OH][FeCl4] is an excellent catalyst for this transformation. Consequently, this is a highly efficient and green protocol for the synthesis of trisindoline derivatives.
Having identified the optimal reaction conditions, we examined the substrate scope of the reaction between indoles (1) and isatins (2) catalyzed by [Dabco‐C2OH] [FeCl4] (10 mol%) in C2H5OH at 50 °C, and the results are listed in Table 3. All the reactions between different substituted indoles (1a‐e) and isatin (2a) proceeded smoothly under the standard reaction conditions and afforded the corresponding trisindolines (3a‐e) in excellent yields (94–98%) within very short reaction times (5–60 minutes) (Table 3, entries 1–5). Isatins with diverse functional groups such halide, methoxyl, methyl and nitro were also tolerated in the present protocol (Table 3 , entries 6–11). When 5‐substituted isatins are employed in the reaction, high yields often obtained within short reaction times (Table 3, entries 6–10). However, when the isatin with other substituent position, such as 4‐bromoisatin, is used in the reaction, a longer reaction time is needed (Table 3, entry 11).
Encouraged by the remarkable results, to further confirm the generality of this approach, we then often extended the method to synthesis of other kinds of bis‐indoles, such as bis (indolyl) methane derivatives. As shown in Table 4, the Friedel–Crafts reaction between indoles and aromatic aldehyde with electron‐ withdrawing or ‐donating groups delivered the desired products in excellent yields (90–98%) under the optimal reaction conditions. Furthermore, the positions and number of substituted group of aromatic aldehydes have no effect on the reaction yields.
It is of interest to further extend the application of this procedure to synthesis of bis‐indoles from aliphatic aldehydes and ketones. The substrates of isobutyraldehyde, cyclopentanone and cyclohexanone were tested in this reaction. As expected, the reactions proceeded well to afford the corresponding products 7a to 7c in good yields. However longer reaction times were needed for the synthesis of 7b and 7c because of the low activity of the aliphatic ketones. The results are represented in Scheme 1.
All the results obtained clearly indicate that we have developed a simple, efficient and high‐yielding general route for the synthesis of a wide variety of densely substituted indole derivatives. On the other hand, C3‐substituted indoles can be prepared by ring‐opening of epoxides with indoles via Friedel–Crafts alkylation which is also an attractive transformation due to its atom economy.[81] Then we examined the ring‐opening reaction between indoles with styrene oxide in presence of 10 mol% [Dabco‐C2OH] [FeCl4] catalyst under neat conditions at 50 °C. As expected, the desirable products 9a‐e were all obtained in good yields (Scheme 2).
The recyclability of the catalyst is one of the most important parameters in chemical production, we investigated the recyclability of this ionic liquid for the synthesis of trisindoline 3a. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C and filtered, then dried to obtain the pure product. The IL catalyst was left in filtrate. After removing the solvent under vacuum, the catalyst could be directly reused in the next recycling run under the same conditions. Even after reusing for six times, this iron‐containing ionic liquid could also drive the reaction and afford the corresponding product in a
high yield (Table 5).
Base on the experimental results, a tentative mechanism for the formation of bis‐indoles is depicted in Scheme 3. Both the anion of [FeCl4]− and Lewis acid FeCl3 play the important roles. The reaction, most probably, starts with the activation of carbonyl group with FeCl3 to form A. Next, an addition reaction may occurred between A and the first molecule of indole to generate ionic intermediate B. Dehydration of C affords the intermediate D which probably undergoes addition with the second molecule of indole to afford the target product 3 and regenerates the catalyst. Other substrates of carbonyl
compounds undergo a similar transformation.
3 | CONCLUSION
In summary, we have successfully developed a novel, efficient and inexpensive iron‐containing IL ([Dabco‐C2OH] [FeCl4]) catalyst for the synthesis of C3‐substituted indole derivatives including trisindolines, bis(3‐indolyl) methanes and β‐indolyl alcohols under mild conditions. A wide range of carbonyl compounds including isatins, aromatic/aliphatic aldehydes and aliphatic ketones with
different substituted indoles can be employed in the reaction, and afford the corresponding trisindoline and bis(3‐indolyl) methane derivatives in excellent yields. It is much superior to other reported synthetic protocols, in terms of its simple operation, short reaction time, excellent yield, absence of any chromatographic separation technique, ease of separation and recyclability of the catalyst. In addition, this efficient protocol was also applied to the synthesis of β‐indolyl alcohols via Friedel–Crafts alkylation of indoles with styrene oxide. Further investigations of the catalysts are still in progress. The
results will be reported soon.
4 | EXPERIMENTAL
4.1 | Materials and instrumentation
All the solvents were used without further purification. Melting points were determined with a RY‐I apparatus and are reported uncorrected. 1 H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AV‐400 spectrometer with DMSO‐d6 or CDCl3 as the solvent. Chemical shifts were calibrated to tetramethylsilane as an external reference. The 1 H NMR data are reported as the chemical shift in parts per million, multiplicity (s, singlet; d, doublet; t, triplet; m, multiplet), coupling constant in hertz, and number of protons. Raman measurements were carried out on an Bruker RFS 100/S Raman spectrometer at a
wavelength of 1046 nm of a Nd:YAG laser. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was carried out on an SDT Q600 simultaneous thermal analyzer.
4.2 | General procedure for the synthesis of trisindolines and bis‐indoles (3, 5 and 7)
A mixture of indoles (1, 2 mmol), carbonyl compounds (1 mmol) and [Dabco‐C2OH][FeCl4] (35 mg, 10 mol%) in ethanol (1.0 mL) was stirred at 50 °C for the appropriate time. Upon completion of the reaction (monitored by TLC), the mixture was cooled to 0 °C, filtered and washed with cold ethanol, then dried to obtain the pure products (3, 5 and 7). In general, no further purification method was required. The IL catalyst was left in filtrate. After removing the solvent under vacuum, the catalyst could be directly reused in the next recycling run under the same conditions.
4.3 | General procedure for the synthesis of β‐indolyl alcohols (9)
A mixture of indoles (1, 1 mmol), styrene oxide (144 mg, 1.2 mmol) and [Dabco‐C2OH][FeCl4] (35 mg, 10 mol%) was stirred at 50 °C for 2 hrs. Then the reaction mixture was diluted with cold water (5 ml) and CH2Cl2 (5 ml), and extracted with CH2Cl2 (2 × 5 ml), the organic phase was washed with brine (5 ml). After the removal of the solvent under reduced pressure, the residue was subjected to chromatography on a silica gel (200–300 mesh) column using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (3:1) as eluent to afford the corresponding products 9. The IL catalyst was left in aqueous phase. After removing the solvent under
vacuum, the catalyst could be directly reused in the next recycling run for the same reaction.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 21302101), and National Training Programs of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates (No. 201810055095). We also thank the Nankai University College of Chemistry for support.
TrimethylsilylacetyleneCatalog No.:AA0034UM CAS No.:1066-54-2 MDL No.:MFCD00008569 MF:C5H10Si MW:98.2184 |
Stannanetetramine,N,N,N',N',N'',N'',N''',N'''-octamethyl-Catalog No.:AA00834M CAS No.:1066-77-9 MDL No.:MFCD00014860 MF:C8H24N4Sn MW:295.0040 |
TETRAKIS(DIETHYLAMINO)TINCatalog No.:AA00834K CAS No.:1066-78-0 MDL No.:MFCD00239515 MF:C16H40N4Sn MW:407.2166 |
Phosphorodithioic acid, O,O-dimethyl ester, ammonium saltCatalog No.:AA00HAS0 CAS No.:1066-97-3 MDL No.:MFCD09753116 MF:C2H10NO2PS2 MW:175.2101 |
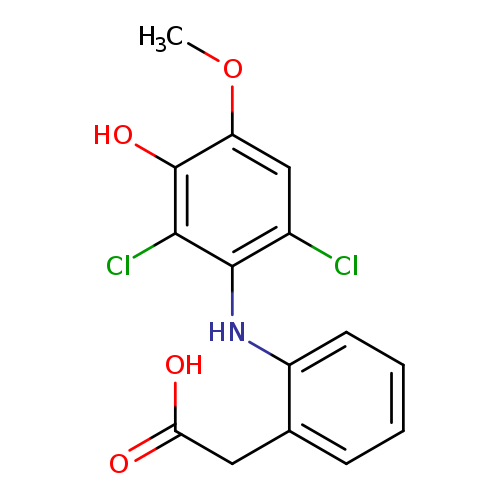
3'-hydroxy-4'-methoxydiclofenacCatalog No.:AA009QD2 CAS No.:106610-60-0 MDL No.: MF:C15H13Cl2NO4 MW:342.1740 |
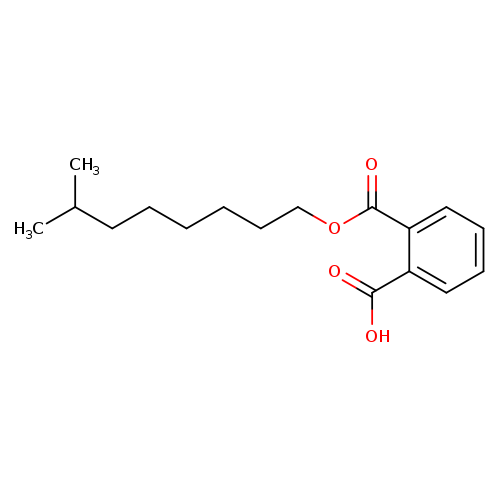
7-Methyl-1-Octanol PhthalateCatalog No.:AA008VRO CAS No.:106610-61-1 MDL No.:MFCD29918078 MF:C17H24O4 MW:292.3701 |
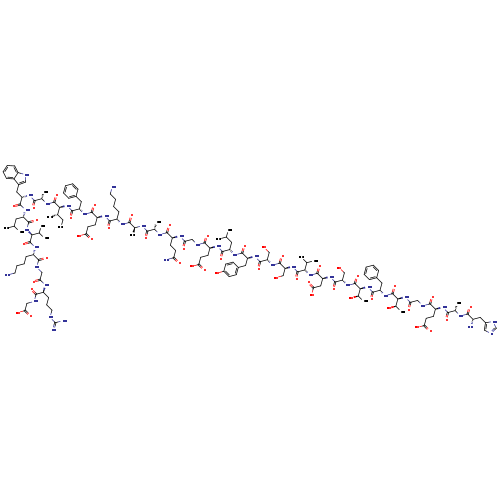
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (Rana catesbeiana), 3-L-glutamicacid-10-L-valine-16-glycine-17-L-glutamine-23-L-isoleucine-24-L-alanine-27-L-valine-31-glycine-32-de-L-lysine-Catalog No.:AA01ENJA CAS No.:106612-94-6 MDL No.:MFCD00167940 MF:C151H228N40O47 MW:3355.6658 |
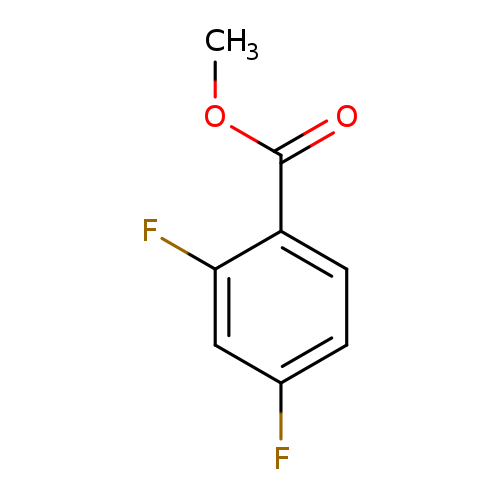
methyl 2,4-difluorobenzoateCatalog No.:AA007UJB CAS No.:106614-28-2 MDL No.:MFCD03093799 MF:C8H6F2O2 MW:172.1288 |
5-Fluoropyrimidine-4,6-diolCatalog No.:AA003MOP CAS No.:106615-61-6 MDL No.:MFCD09033260 MF:C4H3FN2O2 MW:130.0772 |
N-Hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium saltCatalog No.:AA003SZT CAS No.:106627-54-7 MDL No.:MFCD00043100 MF:C4H4NNaO6S MW:217.1324 |
2-Methyl-5-chloromethylpyridine, HClCatalog No.:AA008YC0 CAS No.:106651-81-4 MDL No.:MFCD11111128 MF:C7H9Cl2N MW:178.0591 |
2-Chloro-3-chloromethylpyridine hydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA0092TP CAS No.:106651-82-5 MDL No.:MFCD12923209 MF:C6H6Cl3N MW:198.4775 |
2-(1H-1,2,3-Benzotriazol-1-yl)quinolineCatalog No.:AA01FC3C CAS No.:106653-30-9 MDL No.:MFCD00963413 MF:C15H10N4 MW:246.2667 |
2-Propan-1,1,1,2,3,3,3-d7-amineCatalog No.:AA01CBW9 CAS No.:106658-09-7 MDL No.:MFCD01074299 MF:C3H9N MW:59.1103 |
iso-Propyl-d7-amine HClCatalog No.:AA008SVZ CAS No.:106658-10-0 MDL No.:MFCD01073930 MF:C3H3ClD7N MW:102.6143 |
6,7-Diamino-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzoxazin-3-oneCatalog No.:AA019XA9 CAS No.:106659-52-3 MDL No.:MFCD11205097 MF:C8H9N3O2 MW:179.1760 |
(3-Oxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzoxazin-2-yl)acetic acidCatalog No.:AA0083DM CAS No.:106660-11-1 MDL No.:MFCD00574012 MF:C10H9NO4 MW:207.1828 |
Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-3-[(phenylmethyl)thio]-Catalog No.:AA0083DH CAS No.:106664-91-9 MDL No.:MFCD12132655 MF:C11H14O2S MW:210.2927 |
4-AcetoxynisoldipineCatalog No.:AA008VYY CAS No.:106666-00-6 MDL No.:MFCD09839825 MF:C22H26N2O8 MW:446.4504 |
2-[(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)sulfanyl]ethan-1-amineCatalog No.:AA019WVY CAS No.:106670-25-1 MDL No.:MFCD02763616 MF:C13H15NS MW:217.3299 |
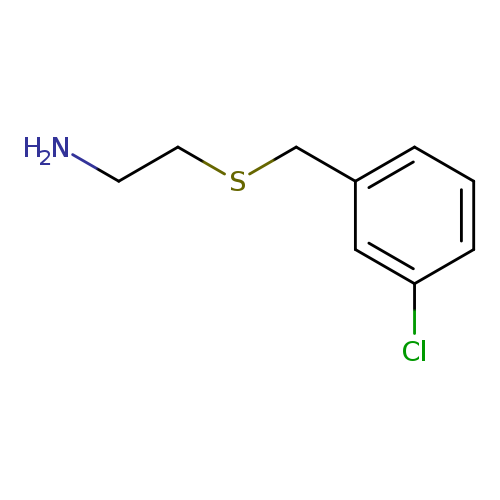
2-[(3-Chlorobenzyl)thio]ethanamineCatalog No.:AA0083DD CAS No.:106670-33-1 MDL No.:MFCD09936842 MF:C9H12ClNS MW:201.7163 |
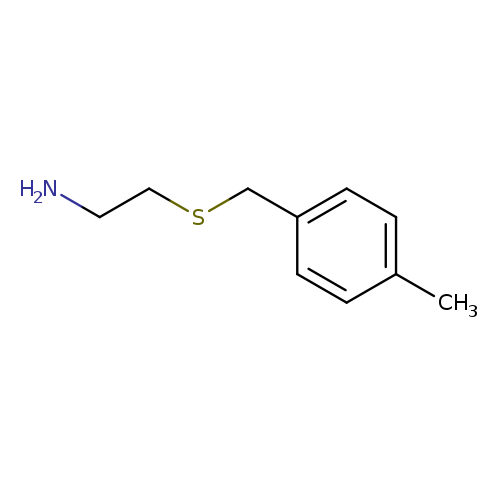
2-[(4-Methylbenzyl)thio]ethanamineCatalog No.:AA0083DC CAS No.:106670-34-2 MDL No.:MFCD06655639 MF:C10H15NS MW:181.2978 |
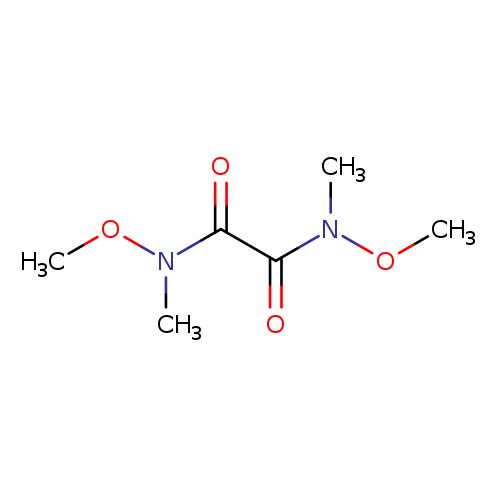
N,N'-Dimethoxy-n,n'-dimethyloxamideCatalog No.:AA003SHH CAS No.:106675-70-1 MDL No.:MFCD02326951 MF:C6H12N2O4 MW:176.1705 |
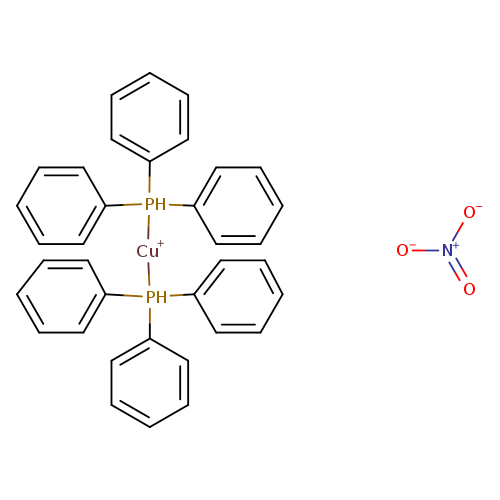
BIS(TRIPHENYLPHOSPHINE)COPPER (I) NITRATECatalog No.:AA008VGC CAS No.:106678-35-7 MDL No.:MFCD02091690 MF:C36H30CuNO3P2 MW:650.1218 |
Diacetato[(S)-(-)-2,2'-bis(di-p-tolylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyl]ruthenium(II)Catalog No.:AA003CLM CAS No.:106681-15-6 MDL No.:MFCD09753021 MF:C52H46O4P2Ru MW:897.9368 |
1-[2-(oxiran-2-yl)ethyl]-1H-pyrroleCatalog No.:AA01C2KK CAS No.:106681-22-5 MDL No.:MFCD12923632 MF:C8H11NO MW:137.1790 |
5,6,7,8-tetrahydroindolizin-7-olCatalog No.:AA01AMSX CAS No.:106681-28-1 MDL No.:MFCD12923630 MF:C8H11NO MW:137.1790 |
7-chloro-8-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolineCatalog No.:AA01BTDU CAS No.:1066822-69-2 MDL No.:MFCD20686792 MF:C10H12ClN MW:181.6620 |
AdapaleneCatalog No.:AA00388Z CAS No.:106685-40-9 MDL No.:MFCD03106112 MF:C28H28O3 MW:412.5201 |
Methyl 6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4-methoxyphenyl]-2-naphthoateCatalog No.:AA007C5Z CAS No.:106685-41-0 MDL No.:MFCD08063923 MF:C29H30O3 MW:426.5467 |
Butanoic acid, 3-oxo-,2-(acetyloxy)-2-methylpropyl esterCatalog No.:AA007UGH CAS No.:106685-66-9 MDL No.:MFCD09753574 MF:C10H16O5 MW:216.2310 |
Butanoic acid,2-[(2-nitrophenyl)methylene]-3-oxo-, 2-(acetyloxy)-2-methylpropyl esterCatalog No.:AA007UGG CAS No.:106685-67-0 MDL No.:MFCD09753528 MF:C17H19NO7 MW:349.3353 |
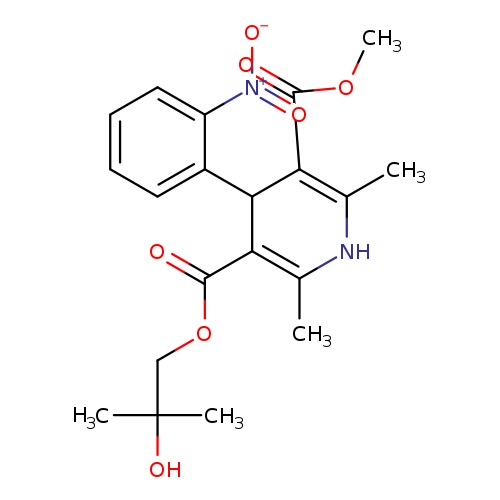
BAY-r-9425Catalog No.:AA008WBP CAS No.:106685-70-5 MDL No.:MFCD09840756 MF:C20H24N2O7 MW:404.4138 |

Ethyl(1-methylbutyl)malonuricAcidCatalog No.:AA01DZF0 CAS No.:106686-60-6 MDL No.: MF:C11H20N2O4 MW:244.2875 |
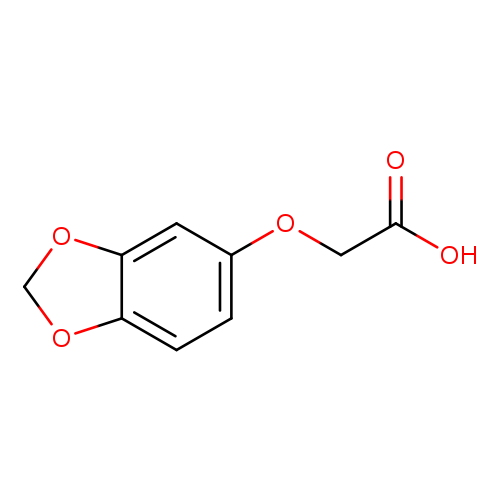
(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)acetic acidCatalog No.:AA007BT3 CAS No.:106690-33-9 MDL No.:MFCD03422207 MF:C9H8O5 MW:196.1568 |
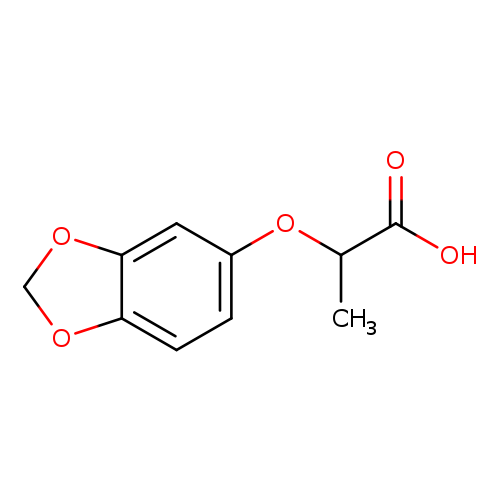
2-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)propanoic acidCatalog No.:AA007BT2 CAS No.:106690-34-0 MDL No.:MFCD03422219 MF:C10H10O5 MW:210.1834 |
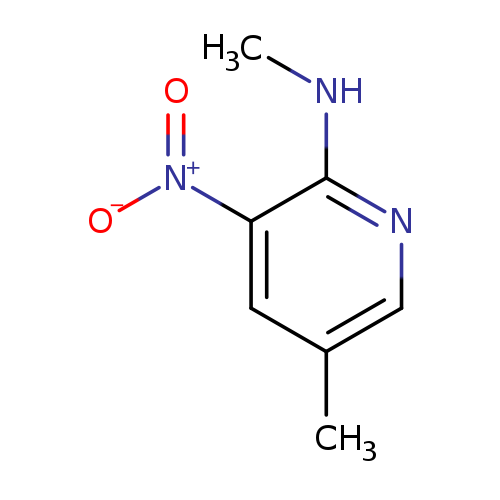
2-Methylamino-5-methyl-3-nitropyridineCatalog No.:AA007UGB CAS No.:106690-38-4 MDL No.:MFCD09862683 MF:C7H9N3O2 MW:167.1653 |
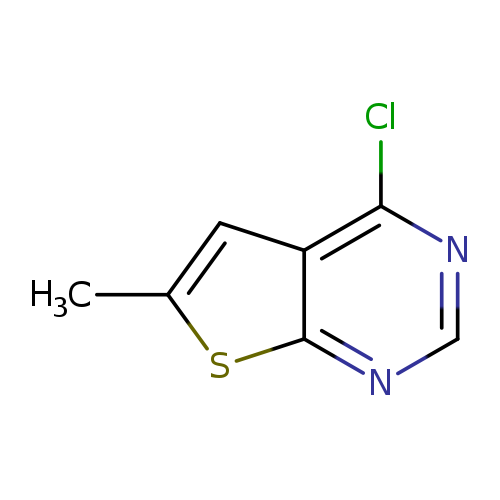
4-Chloro-6-methylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidineCatalog No.:AA007BSZ CAS No.:106691-21-8 MDL No.:MFCD03030440 MF:C7H5ClN2S MW:184.6460 |
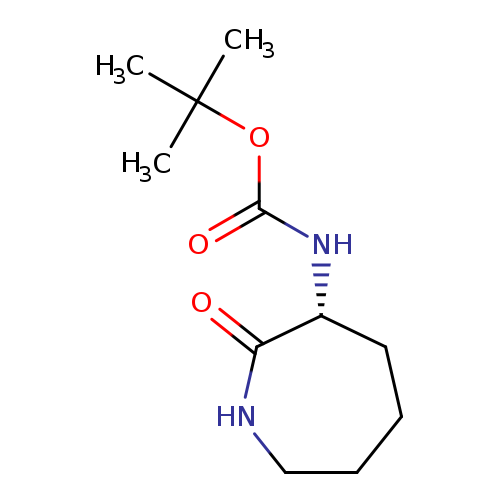
(R)-tert-Butyl (2-oxoazepan-3-yl)carbamateCatalog No.:AA007BSW CAS No.:106691-72-9 MDL No.:MFCD03788637 MF:C11H20N2O3 MW:228.2881 |
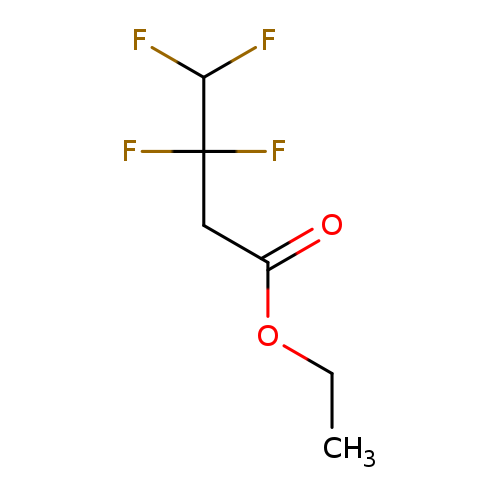
Ethyl 3,3,4,4-tetrafluorobutanoateCatalog No.:AA01F2JV CAS No.:106693-03-2 MDL No.:MFCD25368905 MF:C6H8F4O2 MW:188.1201 |
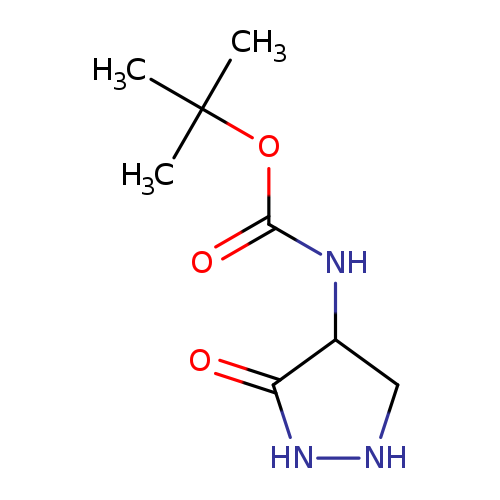
tert-Butyl n-(3-oxopyrazolidin-4-yl)carbamateCatalog No.:AA00HAS3 CAS No.:106693-44-1 MDL No.:MFCD13176501 MF:C8H15N3O3 MW:201.2230 |
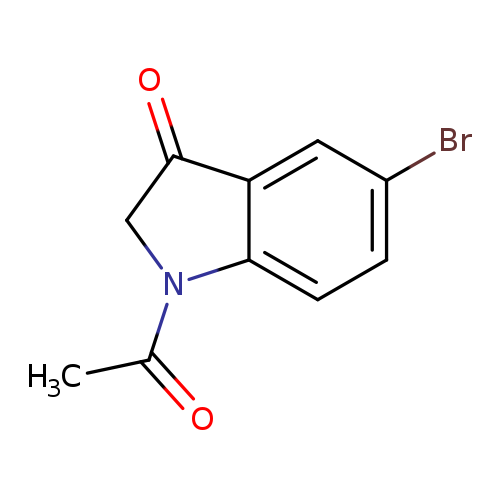
1-Acetyl-5-bromoindolin-3-oneCatalog No.:AA007UFU CAS No.:106698-07-1 MDL No.:MFCD00463385 MF:C10H8BrNO2 MW:254.0800 |
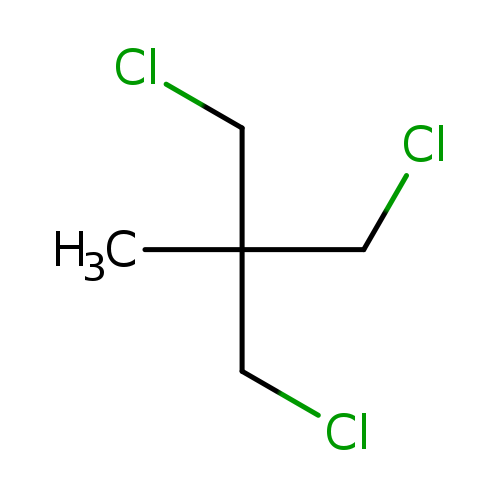
1,1,1-TRIS(CHLOROMETHYL)ETHANECatalog No.:AA003D2Z CAS No.:1067-09-0 MDL No.:MFCD00013686 MF:C5H9Cl3 MW:175.4840 |
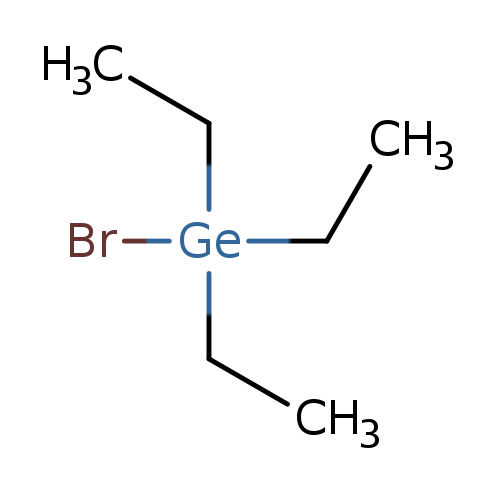
Germane, bromotriethyl-Catalog No.:AA007BSF CAS No.:1067-10-3 MDL No.:MFCD00013513 MF:C6H15BrGe MW:239.7273 |
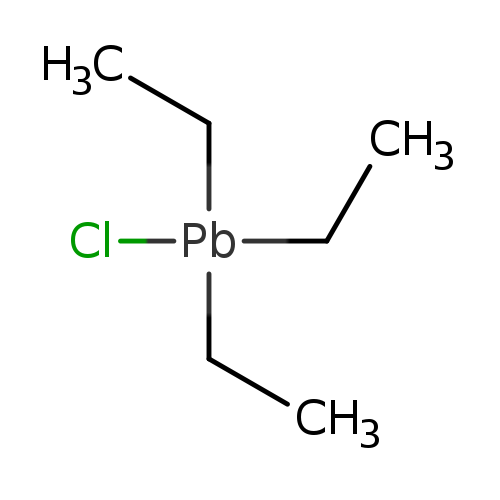
TRIETHYLLEAD CHLORIDECatalog No.:AA008S2U CAS No.:1067-14-7 MDL No.:MFCD00013597 MF:C6H15ClPb MW:329.8363 |
DIMETHYLAMINOTRI-N-BUTYLTINCatalog No.:AA008URD CAS No.:1067-24-9 MDL No.:MFCD00077998 MF:C14H33NSn MW:334.1195 |
Trimethoxy(propyl)silaneCatalog No.:AA003V0C CAS No.:1067-25-0 MDL No.:MFCD00043026 MF:C6H16O3Si MW:164.2749 |
Stannane, bis(acetyloxy)dibutyl-Catalog No.:AA00IKDN CAS No.:1067-33-0 MDL No.:MFCD00008697 MF:C12H24O4Sn MW:351.0176 |
TETRA-N-BUTYLGERMANECatalog No.:AA003UNX CAS No.:1067-42-1 MDL No.:MFCD00015224 MF:C16H36Ge MW:301.0970 |
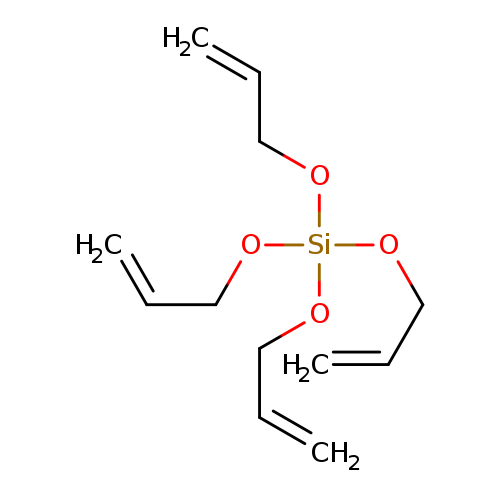
TETRAALLYLOXYSILANECatalog No.:AA003UJE CAS No.:1067-43-2 MDL No.:MFCD00048172 MF:C12H20O4Si MW:256.3703 |
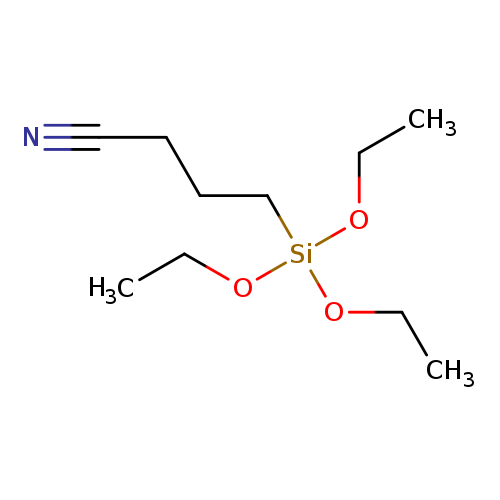
4-(Triethoxysilyl)butanenitrileCatalog No.:AA003J9Q CAS No.:1067-47-6 MDL No.:MFCD00042636 MF:C10H21NO3Si MW:231.3641 |
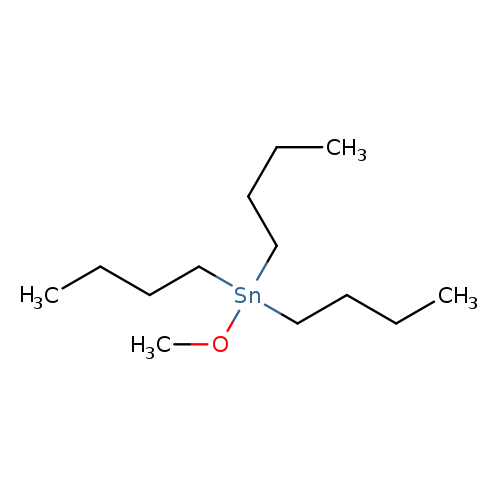
Tri-n-butyltin methoxideCatalog No.:AA0035OQ CAS No.:1067-52-3 MDL No.:MFCD00009419 MF:C13H30OSn MW:321.0777 |
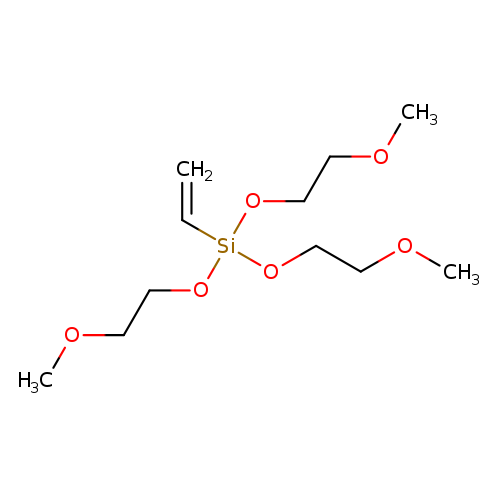
Vinyltris(2-methoxyethoxy)silaneCatalog No.:AA003V8J CAS No.:1067-53-4 MDL No.:MFCD00008500 MF:C11H24O6Si MW:280.3902 |
DibutyldimethoxytinCatalog No.:AA008SMD CAS No.:1067-55-6 MDL No.:MFCD00008345 MF:C10H24O2Sn MW:294.9974 |
N-BUTYLTRIMETHOXYSILANECatalog No.:AA008R33 CAS No.:1067-57-8 MDL No.:MFCD00053675 MF:C7H18O3Si MW:178.3015 |
Diethyl (2-oxopropyl)phosphonateCatalog No.:AA0034N2 CAS No.:1067-71-6 MDL No.:MFCD00044728 MF:C7H15O4P MW:194.1654 |
Diethyl (2-oxobutyl)phosphonateCatalog No.:AA003PBZ CAS No.:1067-73-8 MDL No.:MFCD03427248 MF:C8H17O4P MW:208.1919 |
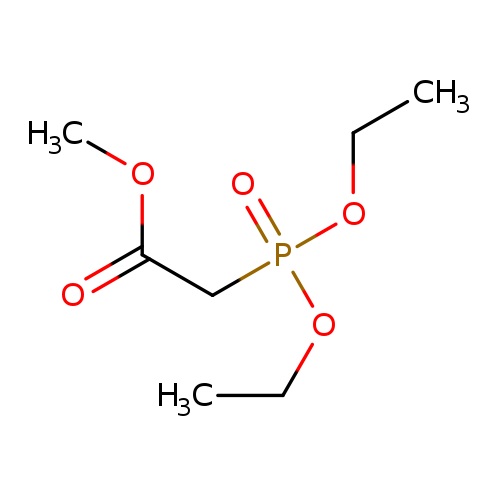
Methyl diethylphosphonoacetateCatalog No.:AA00355X CAS No.:1067-74-9 MDL No.:MFCD00009081 MF:C7H15O5P MW:210.1648 |
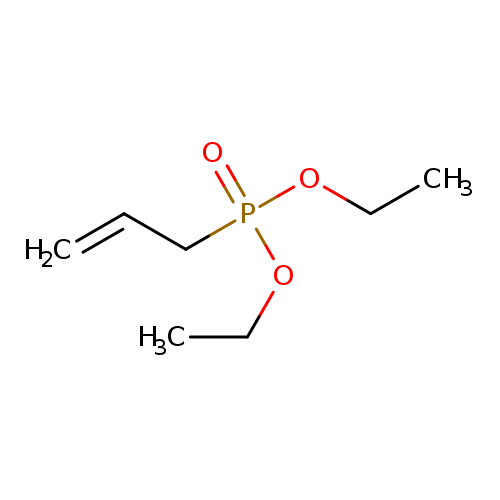
Diethyl allylphosphonateCatalog No.:AA003PDE CAS No.:1067-87-4 MDL No.:MFCD00015134 MF:C7H15O3P MW:178.1660 |
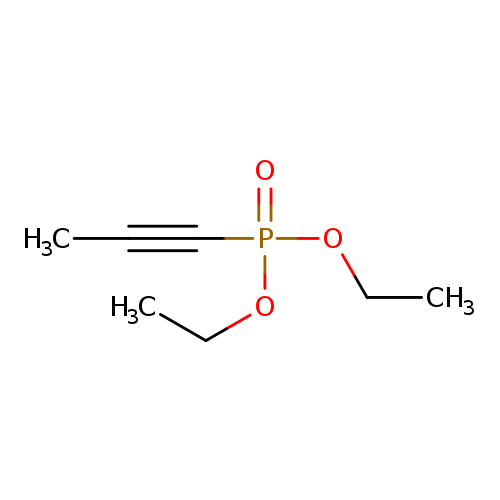
diethyl (prop-1-yn-1-yl)phosphonateCatalog No.:AA019P24 CAS No.:1067-88-5 MDL No.:MFCD00463611 MF:C7H13O3P MW:176.1501 |
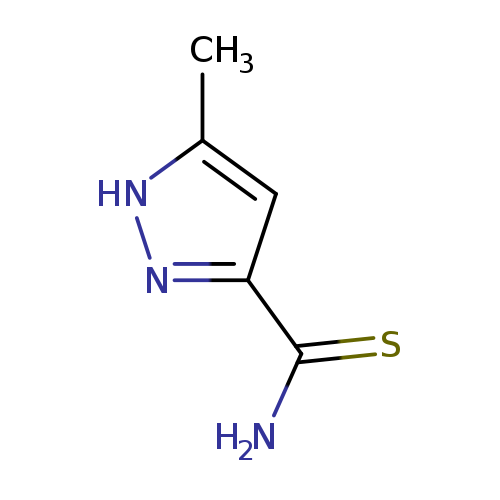
5-METHYL-1H-PYRAZOLE-3-CARBOTHIOAMIDECatalog No.:AA01DX6Z CAS No.:106701-91-1 MDL No.:MFCD19207249 MF:C5H7N3S MW:141.1942 |
Strontium neodecanoate, SrCatalog No.:AA007BSJ CAS No.:106705-37-7 MDL No.:MFCD00070439 MF:C20H38O4Sr MW:430.1333 |
5-Fluoro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazineCatalog No.:AA007BSC CAS No.:1067171-66-7 MDL No.:MFCD11878397 MF:C8H8FNO MW:153.1536 |
2-(Dicyclohexylphosphino)-N,N-bis(1-methylethyl)-1H-indole-1-carboxamideCatalog No.:AA008X2O CAS No.:1067175-36-3 MDL No.:MFCD20257903 MF:C27H41N2OP MW:440.6010 |
2-cyclopentanecarbonylanilineCatalog No.:AA01AK7P CAS No.:106718-47-2 MDL No.:MFCD19982496 MF:C12H15NO MW:189.2536 |
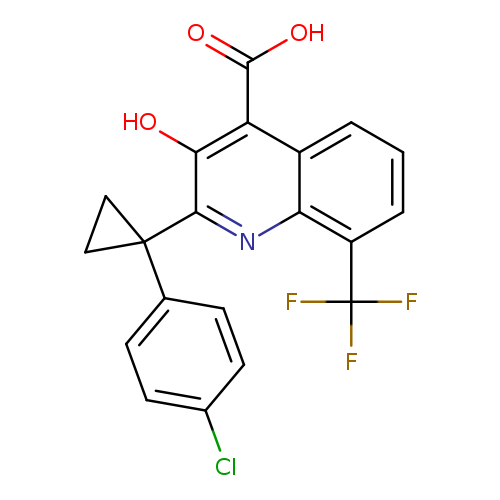
2-(1-(4-Chlorophenyl)cyclopropyl)-3-hydroxy-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline-4-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA019EQO CAS No.:1067186-56-4 MDL No.:MFCD18782752 MF:C20H13ClF3NO3 MW:407.7703 |
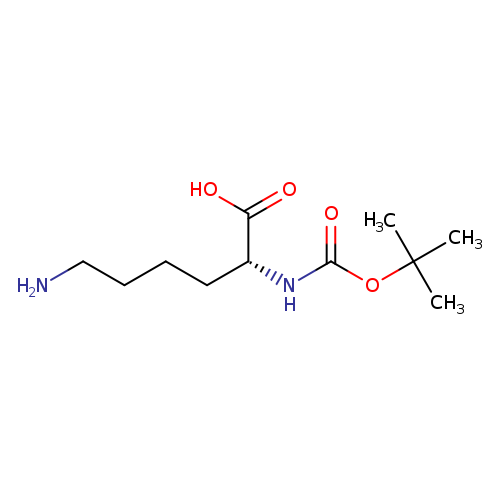
Boc-D-Lys-OHCatalog No.:AA0038WG CAS No.:106719-44-2 MDL No.:MFCD00076956 MF:C11H22N2O4 MW:246.3034 |
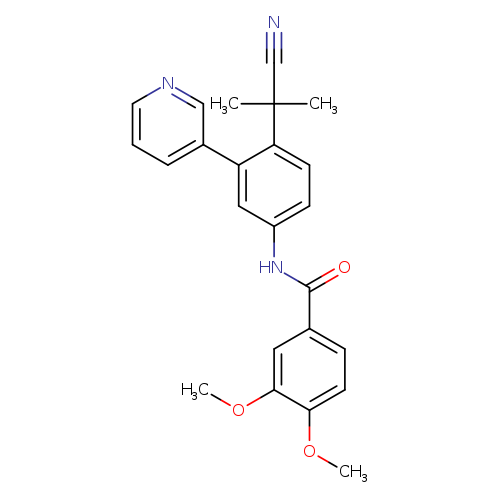
Benzamide, N-[4-(1-cyano-1-methylethyl)-3-(3-pyridinyl)phenyl]-3,4-dimethoxy-Catalog No.:AA003AJL CAS No.:1067191-08-5 MDL No.:MFCD00070623 MF:C24H23N3O3 MW:401.4577 |
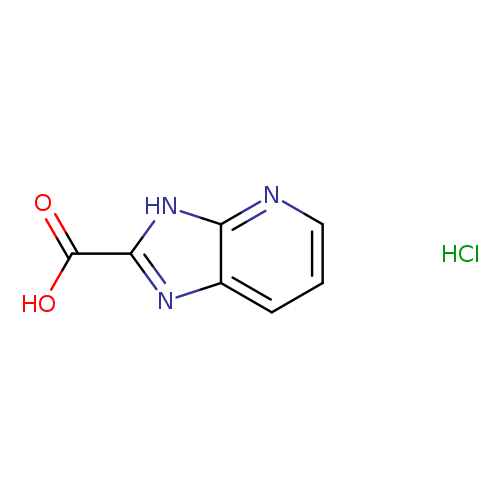
3H-Imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA00J3CE CAS No.:1067193-30-9 MDL No.:MFCD03659971 MF:C7H6ClN3O2 MW:199.5944 |
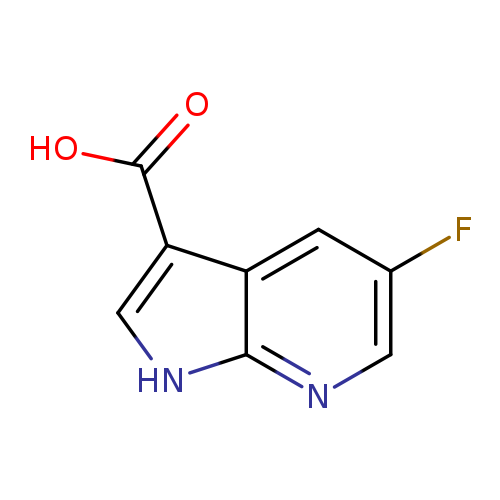
5-Fluoro-7-azaindole-3-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA008XNP CAS No.:1067193-34-3 MDL No.:MFCD12962623 MF:C8H5FN2O2 MW:180.1359 |
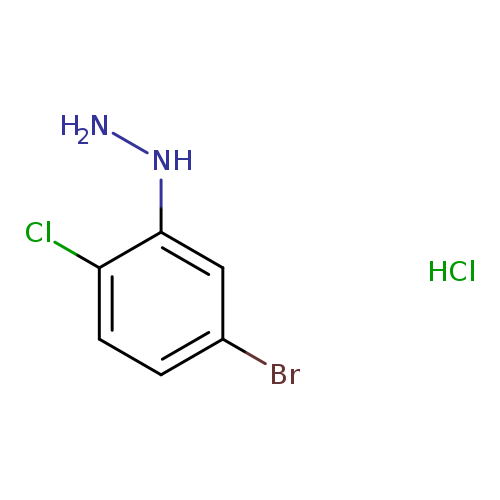
(5-BROMO-2-CHLOROPHENYL)-HYDRAZINE, HYDROCHLORIDECatalog No.:AA01DX70 CAS No.:1067197-15-2 MDL No.:MFCD22123634 MF:C6H7BrCl2N2 MW:257.9432 |
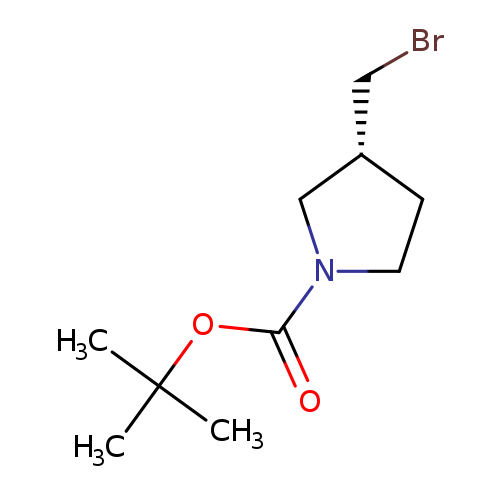
3(R)-Bromomethyl-pyrrolidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl esterCatalog No.:AA008T38 CAS No.:1067230-65-2 MDL No.:MFCD08059335 MF:C10H18BrNO2 MW:264.1594 |
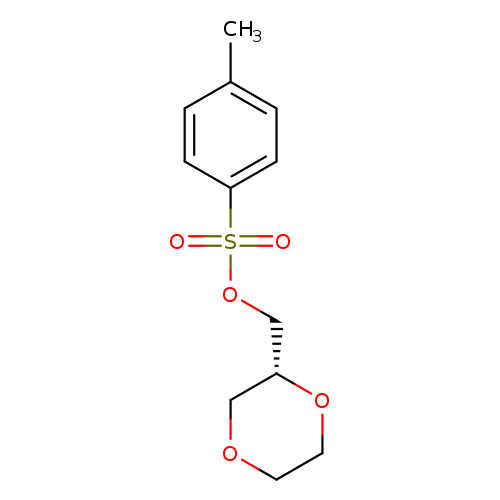
(R)-(1,4-dioxan-2-yl)methyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonateCatalog No.:AA01DX71 CAS No.:1067230-84-5 MDL No.:MFCD22576383 MF:C12H16O5S MW:272.3174 |
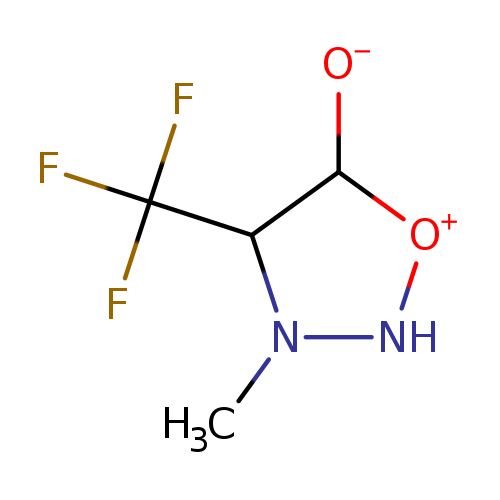
3-Methyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3-oxadiazol-3-ium-5-olateCatalog No.:AA00HAS5 CAS No.:1067233-79-7 MDL No.:MFCD25948961 MF:C4H6F3N2O2 MW:171.0978 |
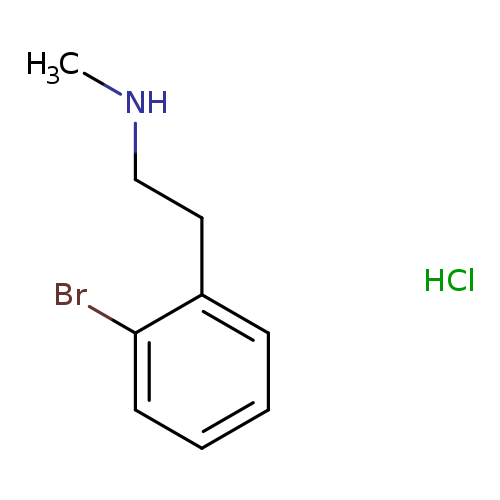
[2-(2-bromophenyl)ethyl](methyl)amine hydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA01BFXV CAS No.:1067237-68-6 MDL No.:MFCD28118789 MF:C9H13BrClN MW:250.5632 |
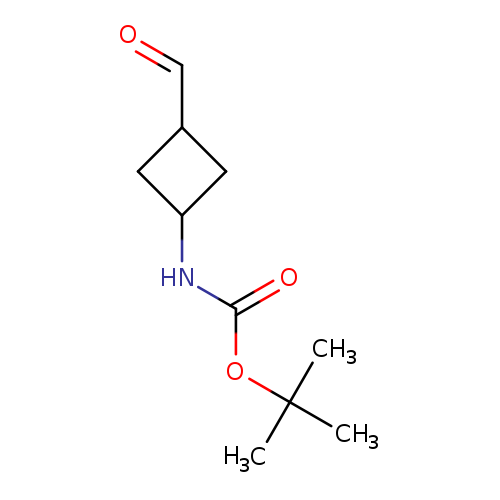
tert-butyl N-(3-formylcyclobutyl)carbamateCatalog No.:AA01BR41 CAS No.:1067239-06-8 MDL No.:MFCD24617807 MF:C10H17NO3 MW:199.2469 |
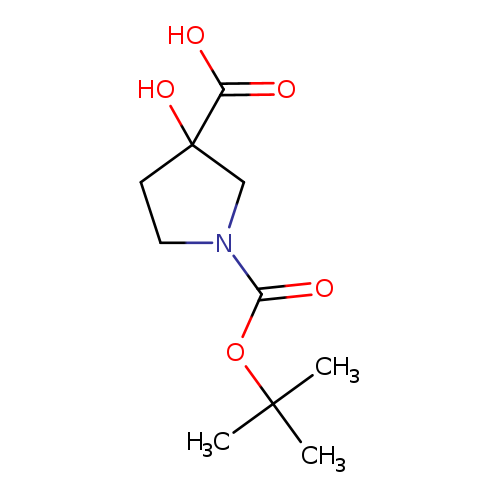
1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-3-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA0096EH CAS No.:1067239-08-0 MDL No.:MFCD15071383 MF:C10H17NO5 MW:231.2457 |
1-Benzyl-3,5-dibromo-1h-1,2,4-triazoleCatalog No.:AA007TYI CAS No.:106724-85-0 MDL No.:MFCD01568839 MF:C9H7Br2N3 MW:316.9800 |

TriethylenetetraMine-d4Catalog No.:AA008VYM CAS No.:1067245-32-2 MDL No.: MF: MW: |
NEODYMIUM NEODECANOATECatalog No.:AA008URC CAS No.:106726-11-8 MDL No.: MF:C30H57NdO6 MW:658.0100 |
5-Cyano-3-pyridinecarboxylic acid methyl esterCatalog No.:AA003RUX CAS No.:106726-82-3 MDL No.:MFCD07367902 MF:C8H6N2O2 MW:162.1454 |
OlprinoneCatalog No.:AA00HAS8 CAS No.:106730-54-5 MDL No.:MFCD25541649 MF:C14H10N4O MW:250.2554 |
(3-Chloro-4-methanesulfonylphenyl)methanamine hydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA01BDUX CAS No.:106737-87-5 MDL No.:MFCD28063724 MF:C8H11Cl2NO2S MW:256.1494 |
3-methyl-4-(methylsulfamoyl)benzene-1-sulfonyl chlorideCatalog No.:AA01BFW6 CAS No.:106738-54-9 MDL No.:MFCD17226536 MF:C8H10ClNO4S2 MW:283.7523 |
GYY 4137Catalog No.:AA007BS1 CAS No.:106740-09-4 MDL No.:MFCD18428020 MF:C15H25N2O3PS2 MW:376.4744 |
Methyl 3-carbamoylbenzoateCatalog No.:AA007BQI CAS No.:106748-24-7 MDL No.:MFCD06245500 MF:C9H9NO3 MW:179.1727 |
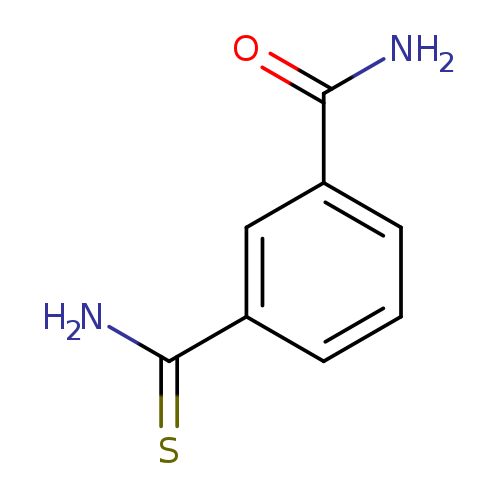
Benzamide, 3-(aminothioxomethyl)-Catalog No.:AA007BQH CAS No.:106748-25-8 MDL No.:MFCD09937067 MF:C8H8N2OS MW:180.2269 |
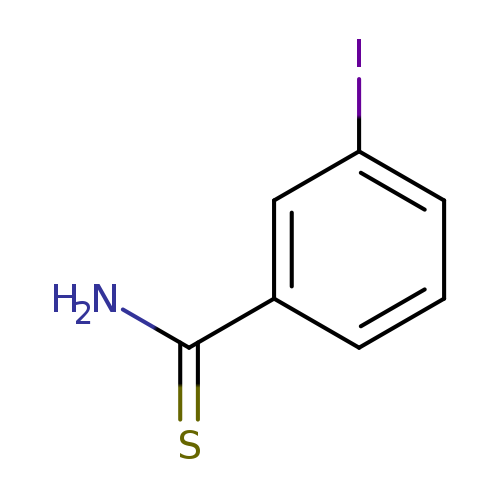
3-IodobenzothioamideCatalog No.:AA007BQG CAS No.:106748-26-9 MDL No.:MFCD04973317 MF:C7H6INS MW:263.0987 |
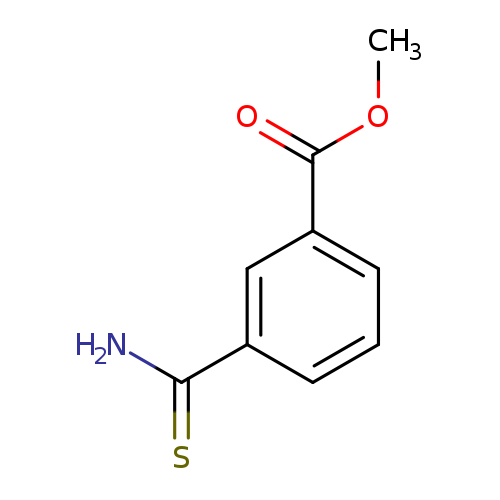
3-(METHOXYCARBONYL)THIOBENZAMIDECatalog No.:AA00831V CAS No.:106748-27-0 MDL No.:MFCD20233581 MF:C9H9NO2S MW:195.2383 |
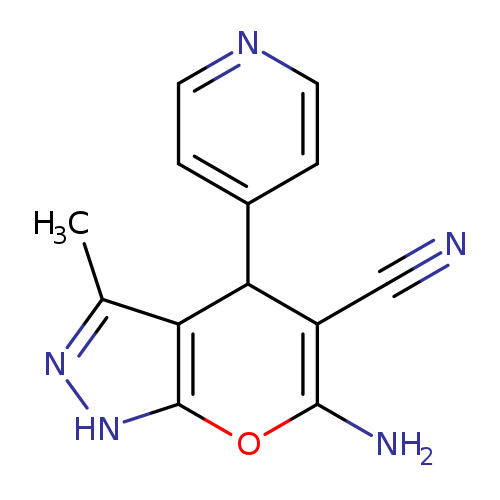
6-Amino-3-methyl-4-(4-pyridinyl)-1,4-dihydropyrano[2,3-c]pyrazole-5-carbonitrileCatalog No.:AA00HASB CAS No.:106753-78-0 MDL No.:MFCD00581077 MF:C13H11N5O MW:253.2593 |
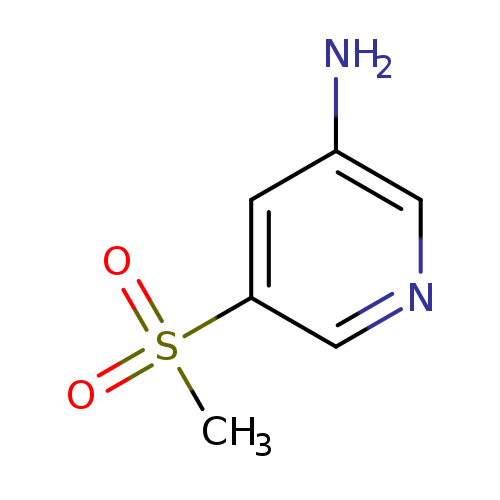
5-(Methylsulfonyl)pyridin-3-amineCatalog No.:AA00942P CAS No.:1067530-19-1 MDL No.:MFCD24642182 MF:C6H8N2O2S MW:172.2049 |
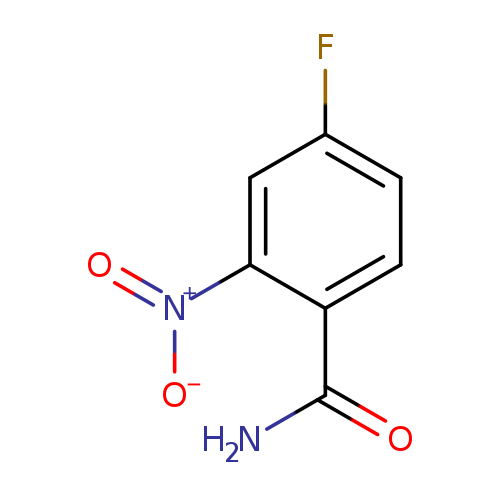
4-Fluoro-2-nitrobenzamideCatalog No.:AA00831K CAS No.:106754-80-7 MDL No.:MFCD04108565 MF:C7H5FN2O3 MW:184.1246 |
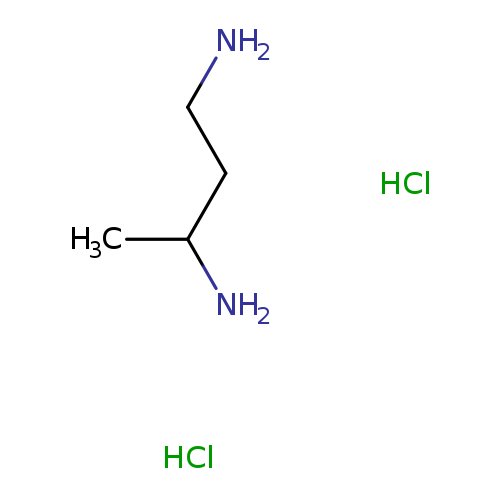
butane-1,3-diamine dihydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA01AKA5 CAS No.:106763-37-5 MDL No.:MFCD19982527 MF:C4H14Cl2N2 MW:161.0734 |
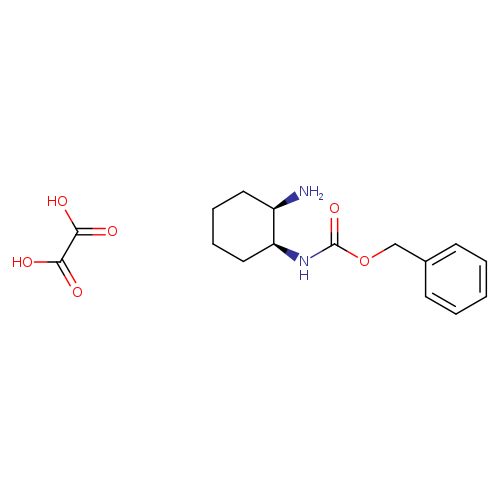
Benzyl (1s,2r)-2-aminocyclohexylcarbamateCatalog No.:AA0096AB CAS No.:1067631-21-3 MDL No.:MFCD11618000 MF:C16H22N2O6 MW:338.3557 |
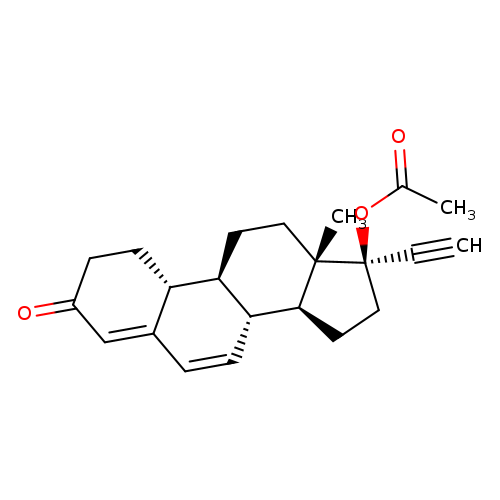
Brn 2173628Catalog No.:AA008UHL CAS No.:106765-04-2 MDL No.:MFCD01711358 MF:C22H26O3 MW:338.4400 |
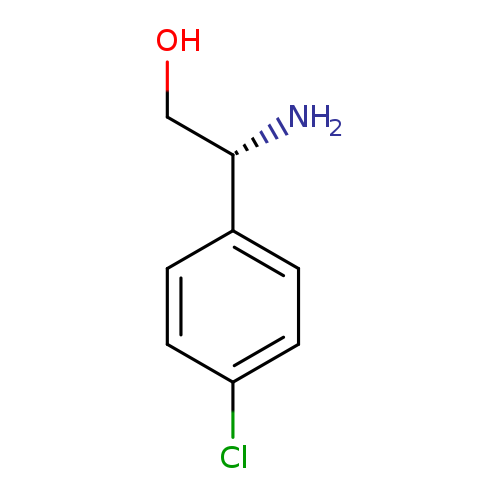
(2R)-2-Amino-2-(4-chlorophenyl)ethan-1-olCatalog No.:AA003AAP CAS No.:1067658-27-8 MDL No.:MFCD09253717 MF:C8H10ClNO MW:171.6241 |
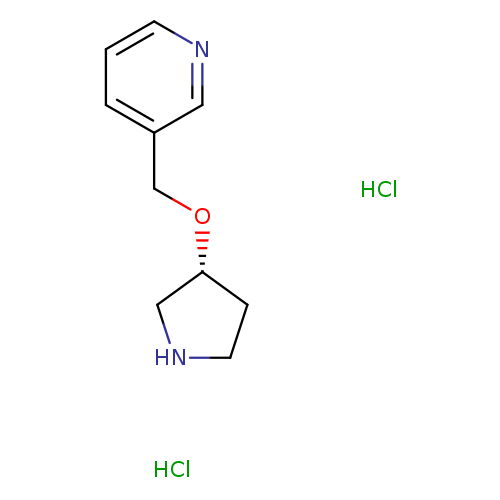
3-([(3R)-Pyrrolidin-3-yloxy]methyl)pyridine dihydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA01BULK CAS No.:1067659-46-4 MDL No.:MFCD30345355 MF:C10H16Cl2N2O MW:251.1528 |
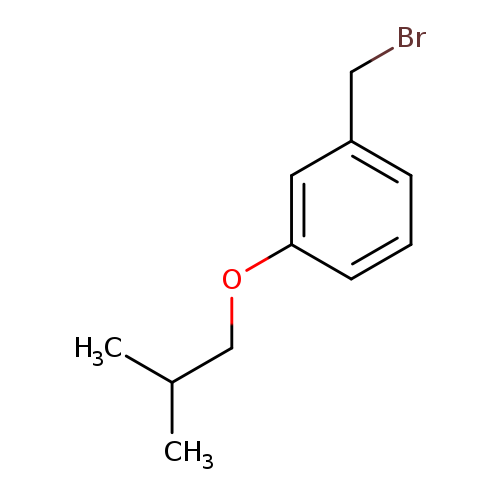
1-(Bromomethyl)-3-(2-methylpropoxy)benzeneCatalog No.:AA01C54E CAS No.:1067678-33-4 MDL No.:MFCD11180490 MF:C11H15BrO MW:243.1402 |
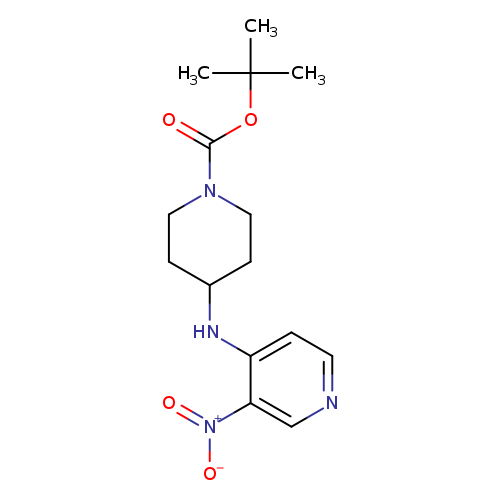
tert-Butyl 4-(3-nitropyridin-4-ylamino)piperidine-1-carboxylateCatalog No.:AA0096ST CAS No.:1067718-07-3 MDL No.:MFCD11974918 MF:C15H22N4O4 MW:322.3596 |
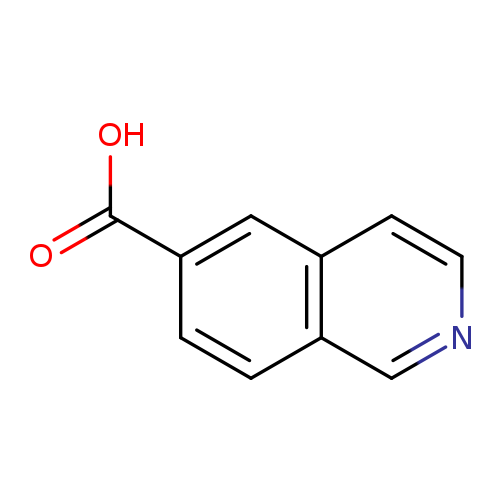
Isoquinoline-6-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA0034AF CAS No.:106778-43-2 MDL No.:MFCD09910323 MF:C10H7NO2 MW:173.1681 |
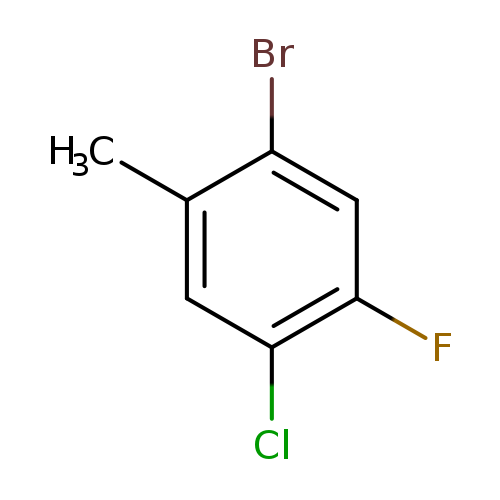
2-Bromo-5-chloro-4-fluorotolueneCatalog No.:AA008Z0B CAS No.:1067882-53-4 MDL No.:MFCD20441895 MF:C7H5BrClF MW:223.4700 |
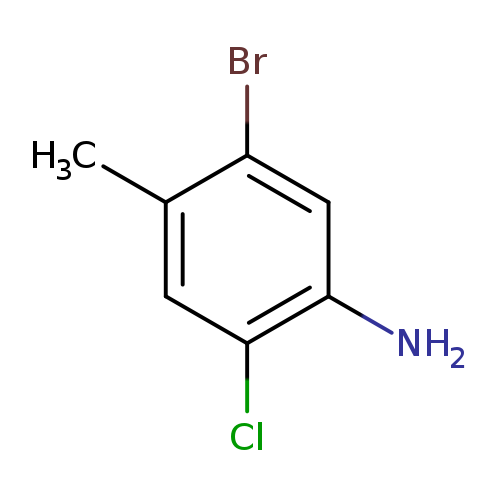
5-bromo-2-chloro-4-methylanilineCatalog No.:AA01C19S CAS No.:1067882-54-5 MDL No.:MFCD29054872 MF:C7H7BrClN MW:220.4942 |
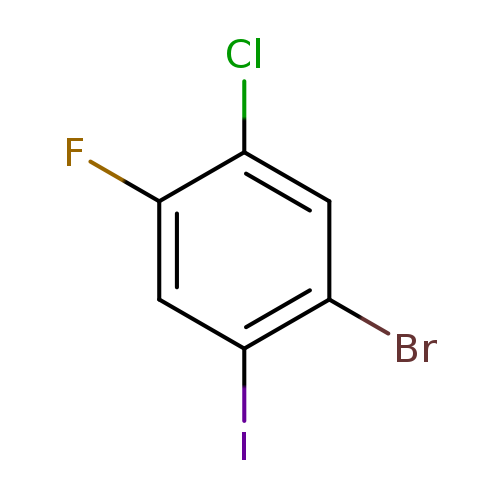
1-Bromo-5-chloro-4-fluoro-2-iodobenzeneCatalog No.:AA0096XD CAS No.:1067882-65-8 MDL No.:MFCD12026232 MF:C6H2BrClFI MW:335.3400 |
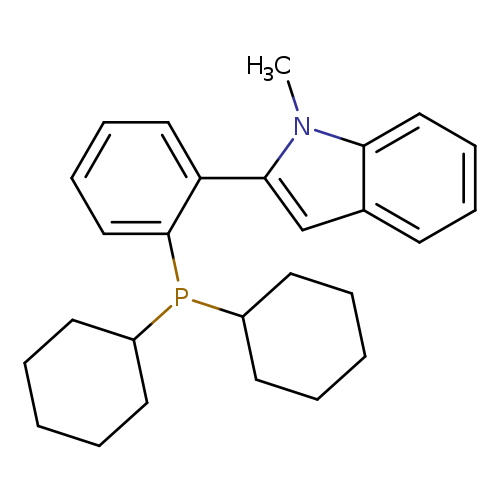
2-(2-(Dicyclohexylphosphino)phenyl)-1-methyl-1h-indoleCatalog No.:AA008U8D CAS No.:1067883-58-2 MDL No.:MFCD16995285 MF:C27H34NP MW:403.5393 |
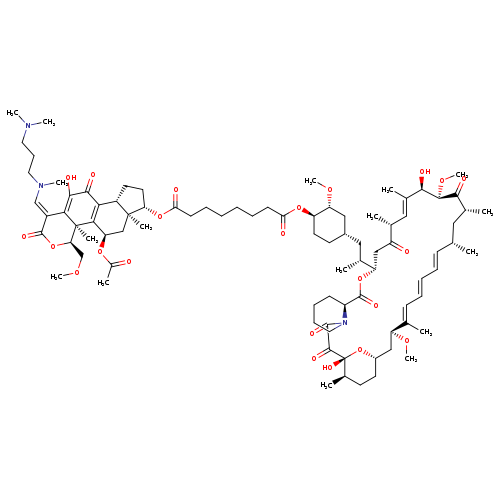
Wortmannin-Rapamycin ConjugateCatalog No.:AA008SQ0 CAS No.:1067892-47-0 MDL No.: MF:C88H131N3O23 MW:1598.9880 |
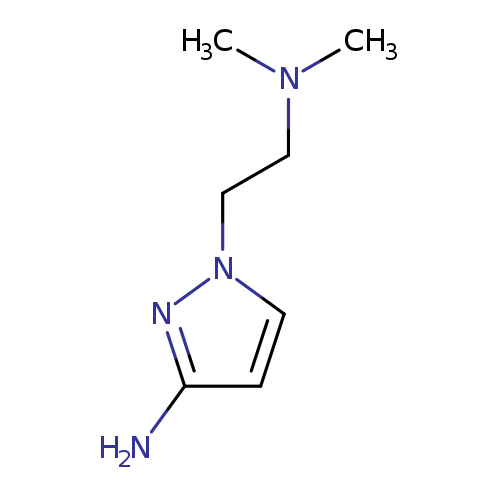
1-(2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-amineCatalog No.:AA01A807 CAS No.:1067900-22-4 MDL No.:MFCD12149376 MF:C7H14N4 MW:154.2129 |
Benzyl 6-chloropyridine-3-carboxylateCatalog No.:AA007TXD CAS No.:1067902-28-6 MDL No.:MFCD11045600 MF:C13H10ClNO2 MW:247.6770 |
(4-methoxyphenyl)(4-methylphenyl)methanamine hydrochlorideCatalog No.:AA019XAV CAS No.:1067902-56-0 MDL No.:MFCD08276233 MF:C15H18ClNO MW:263.7625 |
5-Chloro-6-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylsulfonyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazoleCatalog No.:AA008SZN CAS No.:106791-37-1 MDL No.:MFCD28969705 MF:C14H9Cl3N2O3S MW:391.6569 |
5-bromo-4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidin-2-amineCatalog No.:AA01AQ7L CAS No.:106791-93-9 MDL No.:MFCD16653252 MF:C10H7BrClN3 MW:284.5397 |
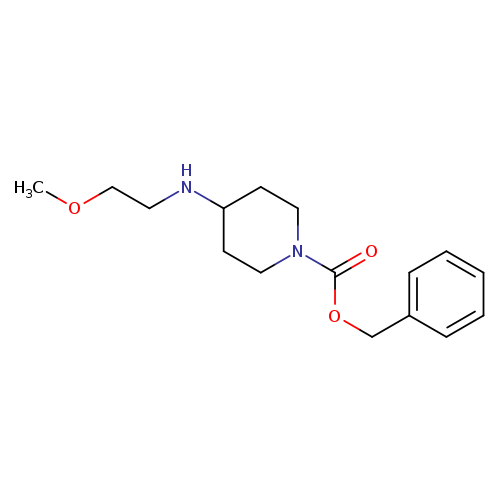
benzyl 4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]piperidine-1-carboxylateCatalog No.:AA01C4ER CAS No.:1067914-64-0 MDL No.:MFCD29763122 MF:C16H24N2O3 MW:292.3734 |
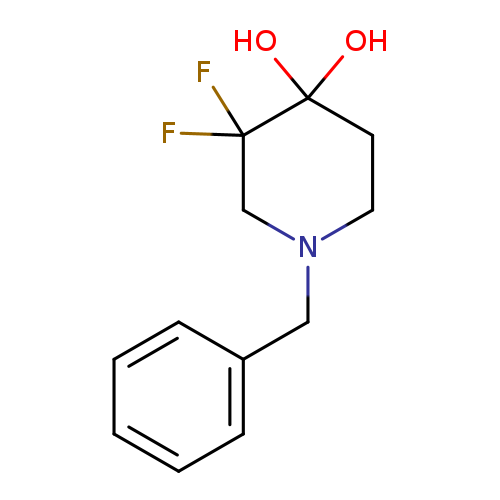
1-Benzyl-3,3-difluoro-4,4-piperidinediolCatalog No.:AA008XN0 CAS No.:1067914-81-1 MDL No.:MFCD20926176 MF:C12H15F2NO2 MW:243.2498 |
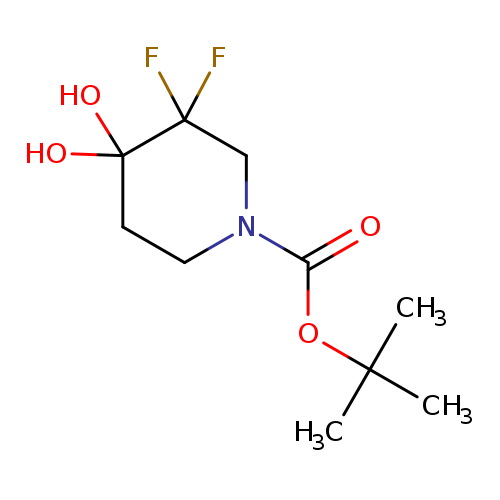
1-Boc-3, 3-difluoro-4,4-(dihydroxy)piperidineCatalog No.:AA0039NH CAS No.:1067914-83-3 MDL No.:MFCD18072968 MF:C10H17F2NO4 MW:253.2431 |
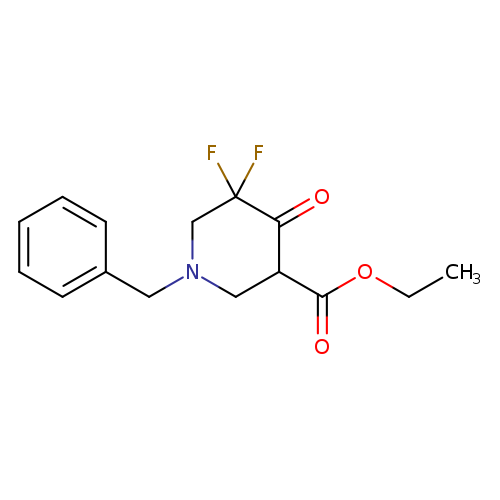
Ethyl 1-benzyl-5,5-difluoro-4-oxopiperidine-3-carboxylateCatalog No.:AA00830Y CAS No.:1067915-34-7 MDL No.:MFCD16036533 MF:C15H17F2NO3 MW:297.2972 |
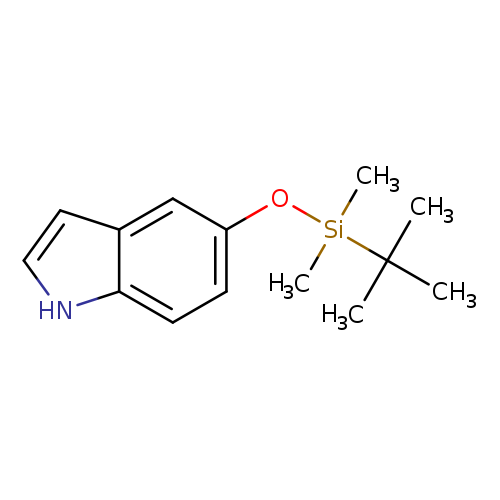
5-(tert-Butyldimethylsilyloxy)-1H-indoleCatalog No.:AA003M05 CAS No.:106792-38-5 MDL No.:MFCD08689500 MF:C14H21NOSi MW:247.4081 |
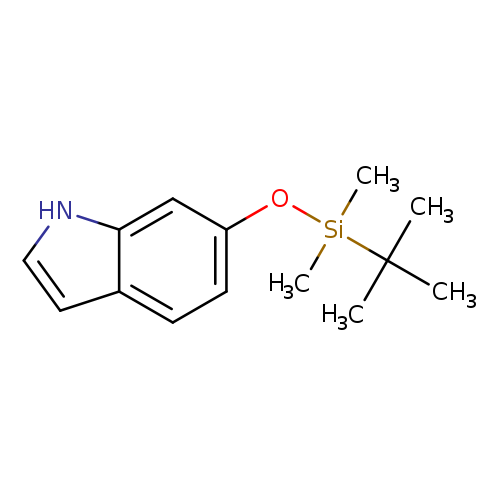
6-[(tert-Butyldimethylsilyl)oxy]-1h-indoleCatalog No.:AA008S2A CAS No.:106792-41-0 MDL No.:MFCD02683922 MF:C14H21NOSi MW:247.4081 |
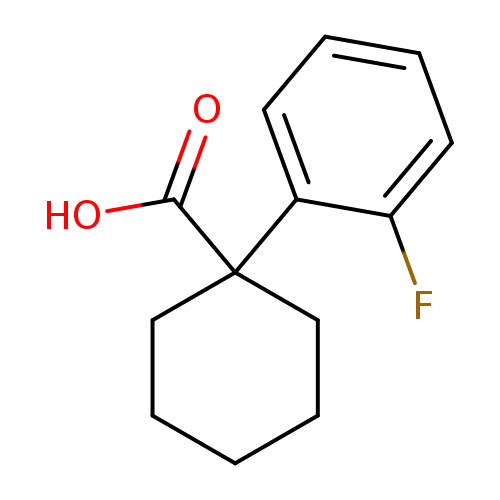
1-(2-fluorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acidCatalog No.:AA007TT0 CAS No.:106795-66-8 MDL No.:MFCD00800623 MF:C13H15FO2 MW:222.2554 |
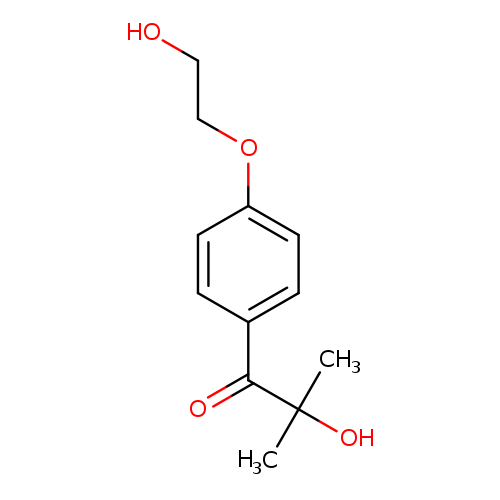
2-Hydroxy-4'-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-2-methylpropiophenoneCatalog No.:AA003B5N CAS No.:106797-53-9 MDL No.:MFCD00085267 MF:C12H16O4 MW:224.2530 |
3-(3-Phenoxyphenyl)propan-1-olCatalog No.:AA007TSY CAS No.:106797-69-7 MDL No.:MFCD09028720 MF:C15H16O2 MW:228.2863 |
1-chloro-2-isocyanato-4-methoxybenzeneCatalog No.:AA019RP1 CAS No.:1067970-63-1 MDL No.:MFCD18269741 MF:C8H6ClNO2 MW:183.5917 |
(2E)-N-methoxy-N-methylpent-2-enamide, ECatalog No.:AA01B6R8 CAS No.:1067975-03-4 MDL No.:MFCD22414382 MF:C7H13NO2 MW:143.1836 |
Diethyl phosphoramidateCatalog No.:AA003PED CAS No.:1068-21-9 MDL No.:MFCD00015676 MF:C4H12NO3P MW:153.1167 |